News
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicinePfizer’s COVID-19 vaccine recommended for adolescents by CDC committee
With the vaccine cleared for high schoolers and many middle schoolers, focus now turns to clinical trials testing COVID-19 vaccines in younger kids.
-
 Neuroscience
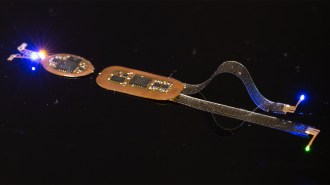
NeuroscienceScientists remotely controlled the social behavior of mice with light
New devices — worn as headsets and backpacks — rely on optogenetics, in which bursts of light toggle neurons, to control mouse brain activity.
-
 Space
SpacePlanet-forming disks around stars may come preloaded with ingredients for life
Methanol spotted around a hot, young star probably originated in interstellar space, suggesting some chemistry for life may start before stars form.
-
 Animals
AnimalsA common antibiotic slows a mysterious coral disease
Applying the antibiotic amoxicillin to infected lesions halted tissue death in corals for at least 11 months after treatment.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHow India’s COVID-19 crisis became the worst in the world
Scientists say a laxed attitude toward masking and social distancing plus the rise of new variants may have fueled India’s coronavirus surge.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceMild zaps to the brain can boost a pain-relieving placebo effect
By sending electric current into the brain, scientists can enhance the pain-relieving placebo effect and dampen the pain-inducing nocebo effect.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyT. rex’s incredible biting force came from its stiff lower jaw
T. rex could generate incredibly strong bite forces thanks to a boomerang-shaped bone that stiffened the lower jaw, a new analysis suggests.
By Sid Perkins -
 Climate
ClimateMangrove forests on the Yucatan Peninsula store record amounts of carbon
Dense tangles of roots and natural water-filled sinkholes join forces to stockpile as much as 2,800 metric tons of carbon per hectare in the soil.
-
 Microbes
MicrobesThese climate-friendly microbes recycle carbon without producing methane
A newly discovered group of single-celled archaea break down decaying plants without adding the greenhouse gas methane to the atmosphere.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomySaturn has a fuzzy core, spread over more than half the planet’s diameter
Analysis of a wave in one of Saturn’s rings has revealed that the planet’s core is diffuse and bloated with lots of hydrogen and helium.
By Ken Croswell -
 Life
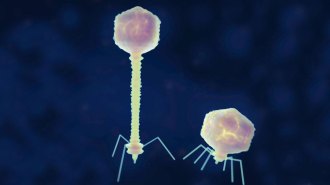
LifeSome viruses thwart bacterial defenses with a unique genetic alphabet
DNA has four building blocks: A, C, T and G. But some bacteriophages swap A for Z, and scientists have figured out how and why they do it.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyA child’s 78,000-year-old grave marks Africa’s oldest known human burial
Cave excavation of a youngster’s grave pushes back the date of the first human burial identified in the continent by at least a few thousand years.
By Bruce Bower