News
-
 Space
SpaceBubble-blowing galaxies could help solve a cosmic mystery
Three galaxies ionizing hydrogen 680 million years after the Big Bang show a potential step in the ionization of nearly all hydrogen in the cosmos.
-
 Climate
ClimateClimate models agree things will get bad. Capturing just how bad is tricky
Climate models are better than ever at simulating complex interactions between ocean, air, ice and land. But scientists still aren’t really sure what the worst-case scenario might be for Earth’s future climate.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHealthy babies exposed to Zika in the womb may suffer developmental delays
A small group of Zika-exposed children in Colombia who were born healthy missed milestones for movement and social interaction by 18 months of age.
-
 Space
SpaceThe home galaxy of a second repeating fast radio burst is a puzzle
The second galaxy known to host brief, brilliant flashes of radio waves known as a recurrent fast radio burst looks nothing like the first.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologySmall ‘cousins’ of T. rex may actually have been growing teenagers
Fossil analyses suggest that Nanotyrannus wasn’t a diminutive relative of the more famous behemoth Tyrannosaurus rex.
By Sid Perkins -
 Astronomy
AstronomyLIGO detects its second neutron star collision, but gains few clues
Gravitational waves have once again heralded a smashup between neutron stars, but this time with no flash of light to help guide understanding.
-
 Earth
EarthClimate change is bringing earlier springs, which may trigger drier summers
An earlier than normal start to spring foliage is associated with drier soils come summer across much, but not all, of the Northern Hemisphere.
-
 Space
SpaceThe first glimpses of a pulsar’s surface hint at complex magnetism
Maps of a rapidly spinning neutron star could eventually help researchers figure out how matter behaves at extraordinarily high densities.
-
 Math
MathColor-changing fibers help reveal mysteries of how knots work
Experiments with colorful fibers helped scientists discover a few simple rules behind knots’ varying strengths.
-
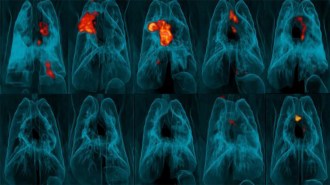 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineInjecting a TB vaccine into the blood, not the skin, boosts its effectiveness
Giving a high dose of a tuberculosis vaccine intravenously, instead of under the skin, improved its ability to protect against the disease in monkeys.
By Tara Haelle -
 Life
LifeRussian foxes bred for tameness may not be the domestication story we thought
Foxes bred for tameness also developed floppy ears and curly tails, known as “domestication syndrome.” But what if the story isn’t what it seems?
By Jake Buehler -
 Life
LifeFluid dynamics may help drones capture a dolphin’s breath in midair
High-speed footage of dolphin spray reveals that droplets blast upward at speeds approaching 100 kilometers per hour.