News
-
 Agriculture
AgricultureFDA to test foods for controversial herbicide
Amid controversy and conflicting studies, the FDA will test food for glyphosate, the most widely used herbicide in the world.
-
 Microbes
MicrobesMissing gut microbes linked to childhood malnutrition
The right mix of gut microbes could prevent kids from succumbing to malnutrition.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyEaster Island people used sharpened stones as tools, not weapons
Sharp-edged stone tools enabled daily survival, not warfare, on Easter Island.
By Bruce Bower -
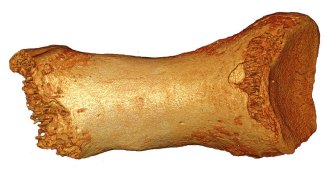 Humans
HumansHuman DNA found in a Neandertal woman
Interbreeding between humans and Neandertals happened earlier than thought, leaving traces in the Neandertal genome.
-
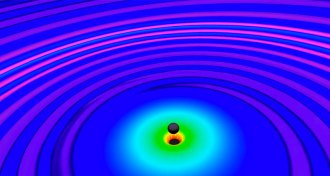 Astronomy
AstronomyBlack hole heavyweights triggered gravity wave event
Those gravity waves came from two black holes more massive than any known outside a galactic core and formed in an environment different than the Milky Way.
-
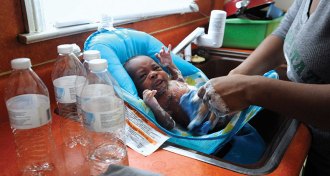 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineLead’s damage can last a lifetime, or longer
Scientists have known for decades that lead is toxic to the brain, but the mark lead exposure leaves on children may actually stretch into adulthood, and perhaps even future generations.
By Meghan Rosen -
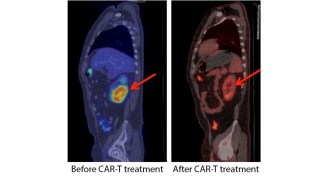 Life
LifeMemory cells enhance strategy for fighting blood cancers
Immune therapy made more powerful with memory T cells.
-
 Animals
AnimalsSaving salamanders from amphibian killer may take extreme measures
Experience from lethal Bd fungus outbreak is helping researchers defend North America’s salamander paradise from new Bsal threat.
By Susan Milius -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceEarly exposure to signing helps deaf kids on mental task
Deaf kids exposed to sign language from birth performed better on a task that required attention and impulse control.
-
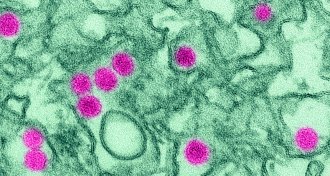 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineUnknowns about Zika virus continue to frustrate
As worry about the Zika virus outbreak continues to ratchet up, scientists are scrambling to understand what threats the virus poses and how to stop it from spreading.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Environment
EnvironmentVaping linked to host of new health risks
Animal studies and analyses of gene activity point to broad range of potential new health risks from vaping affecting everything from sperm to heart and immunity to mental health.
By Janet Raloff -
 Genetics
GeneticsNeandertal DNA may raise risk for some modern human diseases
Neandertal DNA may once have helped humans, but now may contribute to disease.