News
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA new algae-based menstrual pad could stop leaks
By turning period blood into a gel, the pad’s alginate powder filler reduces leakage.
By Claire Yuan -
 Space
SpaceMoonquakes are much more common than thought, Apollo data suggest
The discovery of 22,000 previously unseen moonquakes, plus a new idea of what causes them, could help us better prepare for trips there.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceNASA’s Perseverance rover finds its first possible hint of ancient life on Mars
The NASA Mars rover examined a rock containing organic compounds and “leopard spots” that, on Earth, are associated with microbial life.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyThe North Star is much heavier than previously thought
Polaris is about five times as massive as the sun, new observations reveal. That’s around 50 percent heavier than what an earlier study found.
By Ken Croswell -
 Particle Physics
Particle PhysicsDark matter experiments get a first peek at the ‘neutrino fog’
The hint of fog marks a new way to observe neutrinos, but points to the beginning of the end for this type of dark matter detection.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSepsis tests take days, putting patients at risk. A new method may cut wait time
A faster way to figure out what bacteria is causing a potentially deadly bloodstream infection could let doctors treat it more quickly and efficiently.
By Claire Yuan -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHIV prevention may only require two injections per year
There were no new HIV infections among adolescent girls and young women taking a new PrEP formulation, a twice-yearly shot of the drug lenacapavir.
-
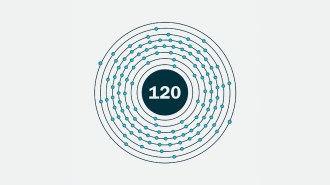 Chemistry
ChemistryA new element on the periodic table might be within reach
Scientists made the known element 116 with a beam of titanium atoms, a technique that could be used to make the undiscovered element 120.
-
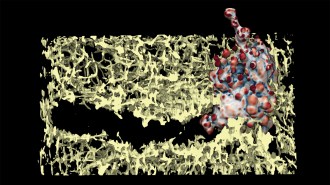 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSome melanoma cancer cells may punch their way through the body
A new study clarifies how melanoma cells use cell membrane protrusions called “blebs” to burrow through tissue.
By Claire Yuan -
 Oceans
OceansIn a seafloor surprise, metal-rich chunks may generate deep-sea oxygen
Instead of sinking from the surface, some deep-sea oxygen may be created by battery-like nodules that split water into hydrogen and oxygen.
By Sid Perkins -
 Space
SpaceA planet needs to start with a lot of water to become like Earth
Rocky planets around fiery stars could hide their water for later use, but it takes 3 to 8 times the amount in our world’s oceans to end up Earthlike.
-
 Physics
PhysicsCan light spark superconductivity? A new study reignites debate
Brief blasts of light might make some materials into fleeting superconductors. Magnetic measurements strengthen the case for this controversial claim.