News
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyYour last-minute guide to the 2024 total solar eclipse
From getting eclipse glasses to checking your weather, we’ve got you covered to help you enjoy this incredible solar eclipse.
By Karen Kwon -
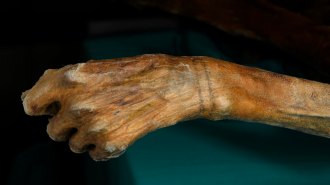
How Ötzi the Iceman really got his tattoos
Modern tattooing experiments challenge a popular idea about how the roughly 5,200-year-old mummified man got marked with dark lines.
By Bruce Bower -
 Chemistry
ChemistryProtein whisperer Oluwatoyin Asojo fights neglected diseases
Oluwatoyin Asojo’s work on hookworm protein structures have contributed to a vaccine being tested in people.
By Carmen Drahl -
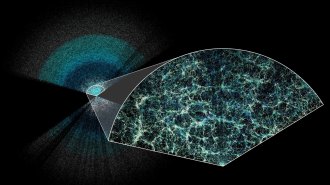 Cosmology
CosmologyThe largest 3-D map of the universe reveals hints of dark energy’s secrets
A year of data from DESI, the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument, suggests that, contrary to expectations, dark energy might vary over time.
-
 Physics
PhysicsPhysicists take a major step toward making a nuclear clock
By tweaking the energy of a thorium nucleus with a laser, scientists demonstrated a key step to building clocks based on the physics of atomic nuclei.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyHow a 19th century astronomer can help you watch the total solar eclipse
Astronomer Maria Mitchell’s observations of total solar eclipses from more than 100 years ago hold tips that are still relevant for watching an eclipse.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBird flu has infected a person after spreading to cows. Here’s what to know
H5N1 has wreaked havoc on birds around the globe and occasionally made the jump to mammals, including cows. The risk to people remains low.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA new study has linked microplastics to heart attacks and strokes. Here’s what we know
Patients with microplastics in their arteries were 4.5 times more likely to have a heart attack, stroke or die within the next three years.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Life
LifeDuring a total solar eclipse, some colors really pop. Here’s why
As a solar eclipse approaches totality and our eyes adjust to dimming light, our color vision changes. It’s called the Purkinje effect.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsHere’s why some pigeons do backflips
Meet the scientist homing in on the genes involved in making parlor roller pigeons do backward somersaults.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceChickadees use memory ‘bar codes’ to find their hidden food stashes
Unique subsets of neurons in a chickadee’s memory center light up for each distinct cache, hinting at how episodic memories are encoded in the brain.
By Jake Buehler -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceHere’s how magnetic fields shape desert ants’ brains
Exposure to a tweaked magnetic field scrambled desert ants’ efforts to learn where home is — and affected neuron connections in a key part of the brain.