Notebook
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceMoon’s lava tubes could be colossal
Lava tubes inside the moon could remain structurally sound up to 5 kilometers across and offer prime real estate for lunar colonists.
-
 Health & Medicine
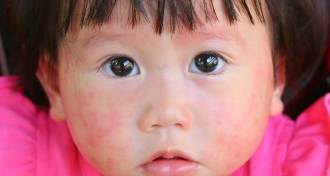
Health & MedicineBirth defects occur in 1 in 10 pregnancies with first trimester Zika infection
About 6 percent of U.S. women infected with Zika virus have infants or fetuses with birth defects, according to preliminary CDC results. For women infected in the first trimester, the number is even higher: nearly 11 percent.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicinePenicillin allergy? Think again.
Most people are either mislabeled with a penicillin allergy or get over it with time, and doctors don’t always think to check.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineOldest traces of smallpox virus found in child mummy
The oldest genetic evidence of smallpox comes from variola virus DNA found in a child mummy buried in a church crypt in Lithuania.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Animals
AnimalsWhy crested penguins lay mismatched eggs
After long migratory swims, crested penguins lay one small and one larger egg.
By Susan Milius -
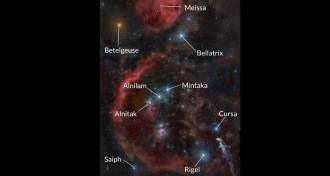 Astronomy
AstronomyGaggle of stars get official names
The names of 227 stars have been formally recognized by the International Astronomical Union.
-
 Life
LifeBlue leaves help begonias harvest energy in low light
The iridescent color of some begonias comes from tiny structures that also help the plant convert dim light into energy.
-
 Microbes
MicrobesCut leaves in bagged salads help Salmonella grow
Juice from torn-up leafy greens helps Salmonella spread in bagged salads.
-
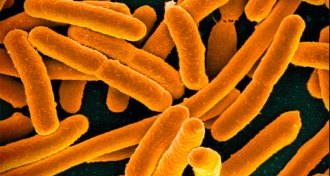 Life
LifeTiny toxic proteins help gut bacteria defeat rivals
A strain of E. coli makes competition-killing tiny proteins and soothes inflamed intestines.
-
 Earth
Earth50 years ago, nuclear blasting for gas boomed. Today it’s a bust.
50 years ago, scientists made plans to use nuclear explosions to extract natural gas from underground. In one such experiment, the gas was released but turned out to be radioactive.
-
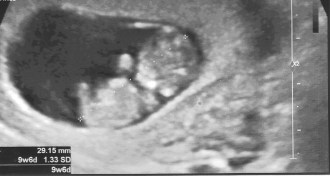 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA Pap smear can scoop up fetal cells for genome testing
Pap smear during pregnancy could offer an early way to test for fetal genetic disorders.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Animals
AnimalsBrazilian free-tailed bats are the fastest fliers
Ultrafast flying by one bat species leaves birds in the dust.