Uncategorized
-

-
 Astronomy
AstronomyWhat can the eclipse tell us about the corona’s magnetic field?
The corona’s plasma jumps and dances thanks to the magnetic field, but scientists have never measured the field directly.
-
 Earth
EarthSeismologists get to the bottom of how deep Earth’s continents go
Scientists may have finally pinpointed the bottoms of the continents.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyCan the eclipse tell us if Einstein was right about general relativity?
During the eclipse, astronomers will reproduce the 1919 experiment that confirmed Einstein’s general theory of relativity.
-
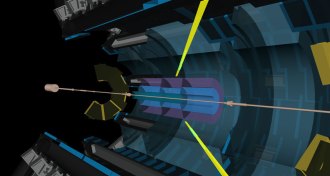 Particle Physics
Particle PhysicsNormally aloof particles of light seen ricocheting off each other
Scientists spot evidence of photons interacting at the Large Hadron Collider.
-
 Life
LifePolluted water: It’s where sea snakes wear black
Reptile counterpart proposed for textbook example of evolution favoring darker moths amid industrial soot.
By Susan Milius -
 Astronomy
AstronomyWhat can we learn about Mercury’s surface during the eclipse?
Instruments aboard twin research jets will take advantage of the total solar eclipse to make the first thermal map of Mercury.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyWhat happens in Earth’s atmosphere during an eclipse?
The charged layer of Earth’s atmosphere gets uncharged during an eclipse, and that could have implications for everything from GPS accuracy to earthquake prediction.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyWhat do plants and animals do during an eclipse?
A citizen science experiment will gather the biggest dataset to date of animal responses to a total eclipse.
-
 Animals
AnimalsWhy midsize animals are the fastest
New analysis delves into the mystery of why medium-sized animals are speedier than bigger ones.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyWhat will scientists learn from the Great American Eclipse?
Between now and August 21, astronomy writer Lisa Grossman will explore the top questions scientists will tackle during the 2017 total solar eclipse.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyWhy is this year’s solar eclipse such a big deal for scientists?
Total eclipses offer scientists a way to see all the way down to the sun’s surface.