Uncategorized
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyOn a mountain in Wyoming, the eclipse brings wonder — and, hopefully, answers
Astronomy writer Lisa Grossman joined scientists on a mountain in Wyoming who were measuring the corona using four different instruments to try to figure out why it’s so hot.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceMars has nighttime snow storms
When clouds of water-ice particles cool at night, snow starts to fall rapidly on Mars, simulations suggest. The squalls could explain observations made by the Phoenix lander in 2008.
-
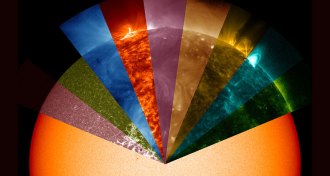 Astronomy
AstronomyEclipse watchers will go after the biggest solar mystery: Why is the corona so hot?
Usually when you move away from a heat source, it gets cooler. Not so in the sun’s atmosphere.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyDoes the corona look different when solar activity is high versus when it’s low?
Carbondale, Ill., will get two eclipses in a row, seven years apart — making it the perfect spot to watch the solar cycle in action.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyCosmic lens lets astronomers zoom in on a black hole’s burps
The beginnings of a jet from an active black hole in a distant galaxy were spotted thanks to a lucky alignment.
-
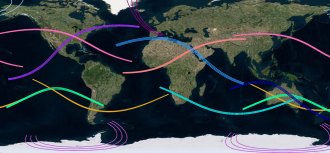 Astronomy
AstronomyHere are the paths of the next 15 total solar eclipses
From 2017 to 2040, there will be 15 total solar eclipses. Here's a map of where to see them.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyWe share the Milky Way with 100 million black holes
New census calculates black hole populations in galaxies big and small.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyWhere does the solar wind come from? The eclipse may offer answers
A quick-fire polarization camera should help scientists detect the origins of the solar wind during the Aug. 21 eclipse.
-
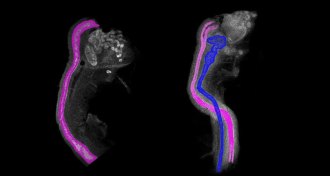 Life
LifeEmbryos kill off male tissue to become female
Female embryos actively dismantle male reproductive tissue, a textbook-challenging study suggests.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceHow an itch hitches a ride to the brain
Scientists have figured out how your brain registers the sensation of itch.
-
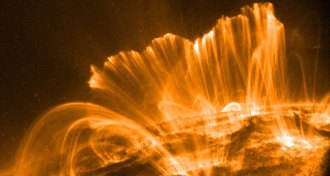 Astronomy
AstronomyWhy are the loops in the sun’s atmosphere so neat and tidy?
Observations during the total solar eclipse may explain why the sun’s atmosphere is so organized despite arising from a tangled magnetic field.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA new tool could one day improve Lyme disease diagnosis
There soon could be a way to differentiate between Lyme disease and a similar tick-associated illness.