See the latest stunning views of Jupiter
The Juno spacecraft whizzes by once every 53 days
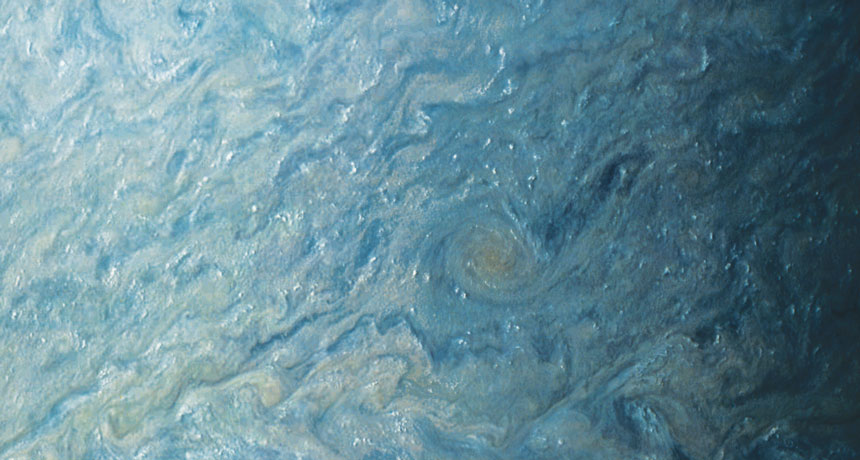

CLOUD TOWERS The tiny white spots in this image of Jupiter’s south tropical zone, taken May 19, 2017, by NASA’s Juno spacecraft, are actually towers of clouds composed of ammonia ice and, perhaps, water ice. Located high in Jupiter’s atmosphere, these towers can stretch about 50 kilometers wide and reach roughly 50 kilometers tall.
NASA, SWRI, MSSS, Gerald Eichstädt, Seán Doran