Uncategorized
-
 Genetics
GeneticsFor penguins, it’s a matter of no taste
Penguins lack taste genes for bitter, sweet and umami.
-
 Tech
TechFacebook detects signs of postpartum depression
An analysis of Facebook activity can identify new moms with postpartum depression.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyGiant hydrogen cloud headed for Milky Way
A high-speed hydrogen cloud on a crash course with the Milky Way appears to be an exotic interloper, preliminary data suggest.
-
 Materials Science
Materials ScienceOld chemistry gives jolt to modern batteries
Chemical reactions discovered in the 19th century improve the performance of futuristic batteries.
-
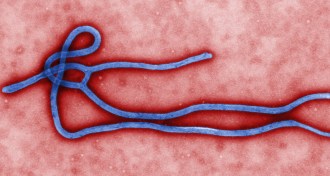 Genetics
GeneticsEbola virus evolution tracked by genetic data
Analysis of Ebola genomes shows how the virus has evolved and some of the mutations that may thwart treatments.
-
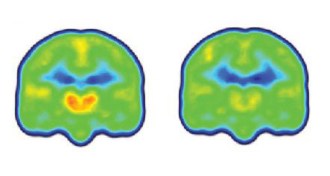 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceChronic pain treatments may get boost from high-tech imaging
Advanced imaging may reveal how well chronic pain treatments work.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineE-cigarettes may be gateway to addiction for teens
Teenagers are using e-cigarettes more than any other tobacco product and for many, it’s the first time they’ve tried a tobacco product at all.
-
 Quantum Physics
Quantum PhysicsQuantum guessing game uses the future to predict the past
Physicists extrapolate forward and backward in time to make accurate predictions about an object’s quantum state at a particular moment.
By Andrew Grant -
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceEnceladus ocean may resemble Antarctic lake
The pH of a subsurface sea on a moon of Saturn resembles an ice-covered lake in Antarctica where microbial mats thrive.
-
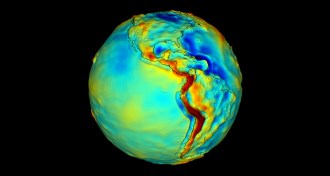 Oceans
OceansOn East Coast, sea levels lean southward
On North America’s East Coast, sea levels tilt slightly downward to the north, new research finds.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineStoplights are hot spots for airborne pollution
Drivers get a big chunk of their exposure to pollutants from short stops at traffic intersections.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyEarliest tree-dweller, burrower join mammal tree of life
Fossils show mammal ancestors did a lot more than cower in dinosaurs’ shadows.
By Susan Milius