Uncategorized
-
 Earth
EarthSometimes value lies deep below the surface
Stories on jellyfish, Ebola, carbon capture's future and heart disease's past reveal how crises old and new often lead to science's healthiest advances.
By Eva Emerson -
 Environment
EnvironmentCarbon capture and storage finally approaching debut
Carbon capture and storage offers a way to rein in global carbon emissions. But financial and regulatory obstacles, as well as public fears, are delaying the technology’s long-awaited implementation.
By Beth Mole -
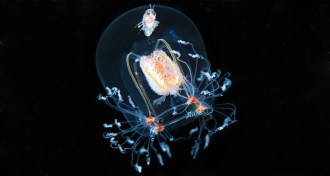 Animals
AnimalsSeeing past the jellyfish sting
Jellies don’t get nearly as much love as their cousins, the corals, but they deserve credit for providing homes to some creatures, dinner to others and more. They’re an integral part of the oceans.
By Susan Milius -
 Materials Science
Materials ScienceMagnets get flipped by light
Controlling magnetism with lasers could lead to faster computer hard drives.
By Andrew Grant -
 Climate
ClimateMultiple oceans may help stall global warming
The Atlantic and Southern oceans, not the Pacific, may be largely to blame for the recent pause in rising global temperatures.
By Beth Mole -
 Animals
AnimalsHummingbirds evolved a strange taste for sugar
While other birds seem to lack the ability to taste sugar, hummingbirds detect sweetness using a repurposed sensor that normally responds to savory flavors.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyDistance to quasars debated
Some astronomers thought quasars were buzzing around our galaxy; turns out these starlike objects live on the other side of the universe.
-
 Ecosystems
EcosystemsLake under Antarctic ice bursts with life
Abundant microbes thrive in subglacial lakes deep under the Antarctic ice sheet.
-
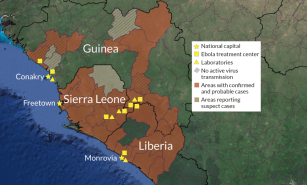 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineExperimental drugs and vaccines poised to take on Ebola
The use of experimental drugs and vaccines against Ebola may turn the tide against an outbreak in Africa that has defied efforts to control it.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Genetics
GeneticsLong before Columbus, seals brought tuberculosis to South America
Evidence from the skeletons of ancient Peruvians shows that seals may have brought tuberculosis across an ocean from Africa.
-
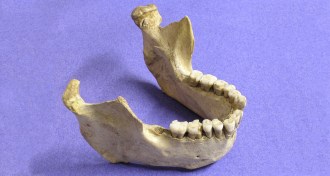 Anthropology
AnthropologyEarlier dates for Neandertal extinction cause a fuss
Revised dates suggest Neandertals coexisted with modern humans for several thousand years in Europe before disappearing 40,000 years ago.
By Bruce Bower -
 Animals
AnimalsOlinguito’s bio built by crowd-sourcing
Crowd-sourcing fleshes out the bio of little-known raccoon relative, the olinguito.
By Susan Milius