Chemistry
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryNanoparticles in foods raise safety questions
As scientists cook up ways to improve palatability and even make foods healthier, some are considering the potential health risks of tiny additives.
By Susan Gaidos -
 Chemistry
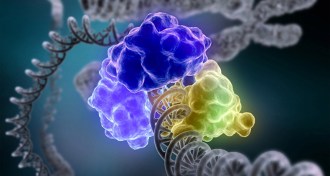
ChemistryChemistry Nobel granted for deciphering DNA repair
Three researchers win chemistry Nobel for working out how cells fix damaged genetic material
By Meghan Rosen and Sarah Schwartz -
 Genetics
GeneticsChemistry Nobel honors studies of DNA repair mechanisms
Studies of DNA’s repair mechanisms have won Tomas Lindahl, Paul Modrich and Aziz Sancar the 2015 Nobel Prize in chemistry.
By Sarah Schwartz and Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineFizzy bubbles carry drugs deep into wounds
Bubble-powered drugs burrow into wounds to stop blood loss.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Chemistry
ChemistryElusive acid finally created
Cyanoform, a chemical sought for more than a century and written into textbooks, is one of the strongest organic acids.
By Beth Mole -
 Chemistry
ChemistrySarah Reisman: Better synthesis of natural compounds
Chemist Sarah Reisman is trying to find new ways to build complicated chemical compounds found in nature.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsDNA architecture, novel forensics offer new clues
Going from theory to practice is always rife with problems, be it shifting from the sequence of DNA’s letters to observing its dynamic machinations or from an identity marker in the lab to a piece of courtroom evidence.
By Eva Emerson -
 Chemistry
ChemistryWanted: Crime-solving bacteria and body odor
Forensic investigators are moving past old-school sleuthing to analyze microbes and odors that tell a more complete story, while pursuing ways to enhance traditional tools as well.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Chemistry
ChemistryThree kids’ science books offer fun, fascinating experiments
No matter what interests kids, there’s a do-it-yourself science book for them. Here are three with entertaining and educational options.
-
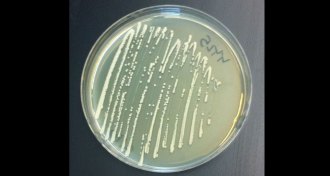 Chemistry
ChemistryPathway pieced together to make opiates in yeast
Scientists have engineered yeast to make sugar into thebaine, a precursor to opiates such as morphine.
-
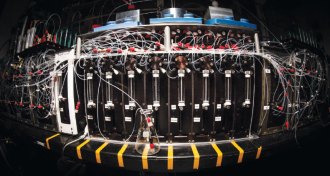 Chemistry
ChemistryAutomated chemistry could build better drugs fast and cheap
Automated molecular synthesis may win over chemists who are not convinced that more technology in drug design is better.
By Beth Mole -
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyMonster fish, forensics and space exploration on display
Exhibits and opera infuse science into their experience.