Earth
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentDeepwater Horizon oil spill caused months-long ‘dirty blizzard’
Pollution from the 2010 Deepwater Horizon oil spill accumulated on the seafloor for months after the leak was patched.
-
 Earth
EarthPioneering geophysicist’s theory of peak oil still debated
The life of geophysicist Marion King Hubbert, creator of the “peak oil” prediction, was intertwined with the politics and science of the oil industry.
-
 Climate
ClimateClimate probably stopped Mongols cold in Hungary
Mongol cavalry was no match for cold, wet climate in medieval Hungary, researchers think.
-
 Climate
ClimateClimate-cooling aerosols can form from tree vapors
Climate-cooling, cloud-seeding aerosols can form in the atmosphere without the sulfuric acid spewed from fossil fuel burning, new research suggests.
-
 Animals
AnimalsAntibiotics in cattle leave their mark in dung
Treating cattle with antibiotics may have side effects for dung beetles, microbes and greenhouse gases.
-
 Physics
PhysicsThe center of Earth is younger than the outer surface
Einstein’s general theory of relativity predicts the center of the Earth is two years younger than the crust.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyYoung sun’s super solar flares helped set early Earth up for life
Super solar flares may have provided early Earth with planet-warming and life-building molecules.
-
 Climate
ClimateZapping clouds with lasers could tweak planet’s temperature
Breaking up the ice particles inside cirrus clouds could make them reflect more light, turning them into a tool to combat global warming.
-
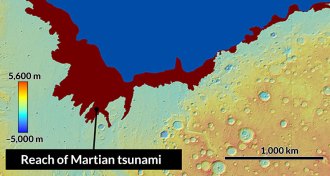 Oceans
OceansAncient tsunamis reshaped Mars’ landscape
Ancient tsunamis generated by meteorite impacts may have reshaped ocean coastlines on Mars.
-
 Oceans
OceansThe Arctic Ocean is about to get spicier
Variations in the saltiness and temperature of seawater of the same density, called spiciness, could increase as the Arctic Ocean warms.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineZika, psychobiotics and more in reader feedback
Readers respond to the April 2, 2016, issue of Science News with thoughts on Zika virus, planetary science, microbes in mental health and more.
-
 Agriculture
AgricultureNew analysis: Genetically engineered foods not a health risk
No real evidence for health or environmental dangers of GE crops.
By Meghan Rosen