Earth
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyYoung sun’s super solar flares helped set early Earth up for life
Super solar flares may have provided early Earth with planet-warming and life-building molecules.
-
 Climate
ClimateZapping clouds with lasers could tweak planet’s temperature
Breaking up the ice particles inside cirrus clouds could make them reflect more light, turning them into a tool to combat global warming.
-
 Oceans
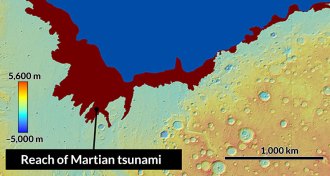
OceansAncient tsunamis reshaped Mars’ landscape
Ancient tsunamis generated by meteorite impacts may have reshaped ocean coastlines on Mars.
-
 Oceans
OceansThe Arctic Ocean is about to get spicier
Variations in the saltiness and temperature of seawater of the same density, called spiciness, could increase as the Arctic Ocean warms.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineZika, psychobiotics and more in reader feedback
Readers respond to the April 2, 2016, issue of Science News with thoughts on Zika virus, planetary science, microbes in mental health and more.
-
 Agriculture
AgricultureNew analysis: Genetically engineered foods not a health risk
No real evidence for health or environmental dangers of GE crops.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Oceans
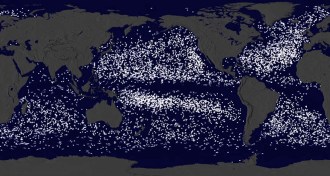
OceansHere’s where 17,000 ocean research buoys ended up
A combined look at 35 years’ worth of ocean buoy movements reveals the currents that feed into ocean garbage patches.
-
 Earth
EarthRemnants from Earth’s birth linger 4.5 billion years later
Shaken, not stirred: Tungsten isotopes reveal that mantle convection has left some remnants of ancient Earth untouched for 4.5 billion years.
By Beth Geiger -
 Environment
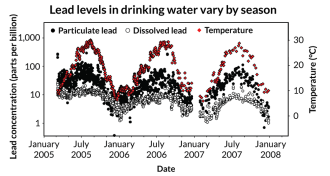
EnvironmentWhen measuring lead in water, check the temperature
Lead contamination in drinking water can be much higher during summer than winter, new research suggests.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentU.S. oil and gas boom behind rising ethane levels
Oil and gas operations on North Dakota’s Bakken shale are largely to blame for a recent rise in global emissions of the greenhouse gas ethane, researchers conclude.
-
 Plants
PlantsHere’s what a leaf looks like during a fatal attack of bubbles
Office equipment beats synchrotrons in showing how drought lets air bubbles kill the water-carrier network of veins in plant leaves.
By Susan Milius -
 Animals
AnimalsCause of mass starfish die-offs is still a mystery
Sea stars off the U.S. west coast started dying off en masse in 2013. Scientists are still struggling to figure out the cause.