Ecosystems
-
 Earth
EarthMineralogy’s link to ecology makes an Earth twin unlikely
Earth’s unique blend of minerals emerged with the evolution of life, making it extremely unlikely that another planet has Earth’s exact mineral composition.
-
 Climate
ClimateResilience protects corals from hurricanes — and climate change
Coral reefs have evolved to be resilient in the face of hurricanes that can devastate human populations. But climate change is reducing the ability of reefs to bounce back from disaster.
-
 Animals
AnimalsScientists’ tags on fish may be leading seals to lunch
In an experiment, 10 young grey seals learned to associate the sound of a pinging tag with fish. The tags may make fish vulnerable to predators, scientists say.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentSpiders enlisted as pollution sensors for rivers
Hunting arachnids provide a better picture of chemical threats to food web.
By Beth Mole -
 Life
LifeA little good news for giant tortoises in the Galapagos
The giant tortoise population on the Galapagos island of Española is on the rebound, but there are still concerns about other markers of conserving the endangered species.
-
 Animals
AnimalsSouthern birds may be moving into your winter backyard
A warming climate is letting warm-adapted birds live farther north in winter, a new study finds.
-
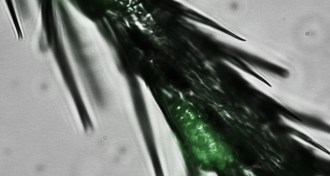 Genetics
GeneticsYeast smell underpins partnership with fruit flies
Yeast make fruity aromas that draw flies, which disperse the fungi. Researchers reveal the gene that underpins the mutually beneficial relationship.
-
 Ecosystems
EcosystemsHelp scientists find floating forests of kelp
By looking for signs of kelp in satellite images, citizen scientists can help researchers keep track of the world’s seaweed forests.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentHuman ingenuity takes on Mother Nature in ‘The Big Ratchet’
Geographer Ruth DeFries explains how technological innovations have allowed humans to overcome environmental challenges throughout history.
-
 Animals
AnimalsInvasive rabbitfish team up to raze algal forests
Tropical rabbitfish have expanded into temperate Mediterranean waters, where they destroy algae forests by gobbling both young and adult algae.
-
 Animals
AnimalsEven on remote islands, busy ports mean more invasives
Islands with lots of trading ties are more likely to be colonized by invasive species, even when they are geographically remote, a new study of anoles reveals.
-
 Life
LifeFledgling birds change rules for caterpillar color
An unusual experiment shows that larvae lose the advantage of warning colors during the seasonal flush of naïve predators.
By Susan Milius