Health & Medicine
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCan humans get chronic wasting disease from deer?
Tests on brain organoids suggest the disease-causing prions face a tough barrier to infect people, but ruling out transmission is a difficult task.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWildfire smoke may cause tens of thousands of premature deaths
A modeling study of California wildfires from 2008 through 2018 estimates that smoke exposure was responsible for as many as 55,700 premature deaths.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBird flu can infect cats. What does that mean for their people?
Pet owners can take precautions to avoid H5N1, such as keeping cats indoors and making sure they don’t eat raw meat or milk.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicinePrivacy remains an issue with several women’s health apps
Inconsistent privacy policies and dodgy data collection in popular fertility and pregnancy tracking apps put women’s health information at risk.
By Payal Dhar -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMalnutrition’s effects on the body don’t end when food arrives
Children may struggle with inflammation, a weakened immune system and gut problems. New treatments may repair some damage.
-
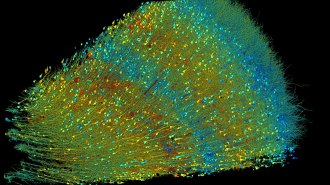 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBiological puzzles abound in an up-close look at a human brain
Mirror-image nerve cells, tight bonds between neuron pairs and surprising axon swirls abound in a bit of gray matter smaller than a grain of rice.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineYoung people’s use of diabetes and weight loss drugs is up 600 percent
Young people’s use of diabetes and weight loss drugs like Ozempic and Wegovy is surging, especially among females ages 18 to 25.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceTwo distinct neural pathways may make opioids like fentanyl so addictive
A study in mice looked at how feelings of reward and withdrawal that opioids trigger play out in two separate circuits in the brain.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHuman body lice could harbor the plague and spread it through biting
Rats and fleas previously got all the blame, but humans’ own parasites could be involved.
-
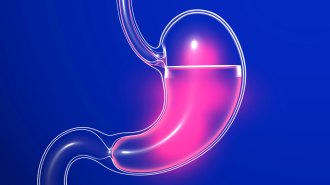 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBurning the stomach lining reduces the ‘hunger hormone’ and cuts weight
An experimental weight loss procedure blasts the stomach lining with heat to curb hunger and cut pounds.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineGenetic analyses of the bird flu virus unveil its evolution and potential
The H5N1 outbreak in cattle is giving flashbacks to the COVID pandemic. But this time is different.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineExtreme heat will put millions more older adults at risk in the future
By 2050, as many as an additional 246 million adults 69 and older could experience temperature extremes that exceed 37.5° Celsius.