Health & Medicine
-
 Health & Medicine
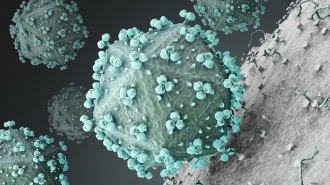
Health & MedicineAn experimental HIV vaccine failed a key trial in South Africa
A vaccine against the human immunodeficiency virus tested in South Africa did not reduce the risk of infection with the virus.
-
 Health & Medicine
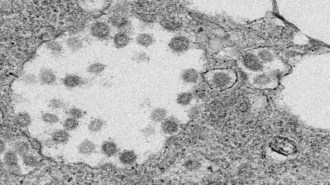
Health & MedicineSARS and the new coronavirus target the same cellular lock to infect cells
Experiments with living cells grown in the lab show that 2019-nCoV enters cells the same way as SARS.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineScientists question White House measures to limit spread of coronavirus
The White House announced new steps to fight the coronavirus outbreak, in what’s becoming one of the biggest public health challenges in decades.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThe first case of coronavirus being spread by a person with no symptoms has been found
Coronavirus cases among coworkers in Germany suggest that the virus can spread from person to person before symptoms appear, similar to the flu.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & Medicine50 years ago, scientists debated the necessity of a smallpox vaccine
In 1970, scientists debated the necessity of routine smallpox vaccinations as the disease declined. Fifty years later, the debate continues.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWHO declares coronavirus outbreak a global public health emergency
The World Health Organization says the coronavirus outbreak that began in China has been reported in 18 other countries.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineStem cell clinics’ much-hyped treatments lack scientific support
Stem cell treatments for knee pain are strong on marketing, weak on science.
By Laura Beil -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineYour most pressing questions about the new coronavirus, answered
As the new coronavirus outbreak unfolds, we are updating this FAQ with the latest on the race to understand the virus and stop the growing global health crisis. Our most recent update was posted February 18.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCan the coronavirus outbreak be contained?
More than 50 million people are quarantined in China, but whether the strategy will stem the epidemic’s spread is unclear.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHow one woman became the exception to her family’s Alzheimer’s history
A single mutation in a woman who evaded Alzheimer’s may point to new ways to treat the disease.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHow the new coronavirus stacks up against SARS and MERS
Coronaviruses are a diverse family that may be becoming more threatening to people.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineLevels of certain proteins in the blood may act as concussion biomarkers
College athletes who suffered concussions had elevated blood levels of three proteins, a potential chemical sign that one day may aid diagnosis.