Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Anthropology
Anthropology‘Slam-dunk’ find puts hunter-gatherers in Florida 14,500 years ago
Finds at an underwater site put people in Florida a surprisingly long time ago.
By Bruce Bower -
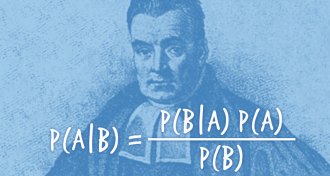 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBayesian reasoning implicated in some mental disorders
An 18th century math theory may offer new ways to understand schizophrenia, autism, anxiety and depression.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBrain waves in REM sleep help store memories
Mice with disturbed REM sleep show memory trouble.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineEarly work on human growth hormone paved way for synthetic versions
In 1966, researchers reported the complete chemical structure of human growth hormone. Today synthetic growth hormone is used to treat growth hormone deficiency.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHealthiest weight just might be ‘overweight’
The body mass index tied to lowest risk of death has risen since the 1970s. It now falls squarely in the “overweight” category.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMouse studies link Zika virus infection to microcephaly
Three new studies in mice shore up the link between microcephaly and Zika virus infection.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThis week in Zika: First mouse study proof that Zika causes microcephaly
Three new studies in mice shore up the link between microcephaly and Zika virus infection.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHeartburn drugs can damage cells that line blood vessels
A type of heartburn drugs called proton pump inhibitors may damage cells that line the blood vessels. The results, though controversial, hint at an explanation for PPI’s link to serious side effects, including risk of dementia and heart attack.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Animals
AnimalsHistory of road-tripping shaped camel DNA
Centuries of caravan domestication and travel left some metaphorical tire marks on Arabian camel genes, researchers find.
-
 Environment
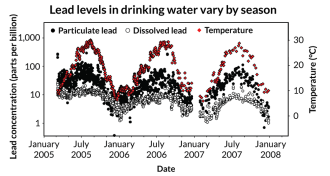
EnvironmentWhen measuring lead in water, check the temperature
Lead contamination in drinking water can be much higher during summer than winter, new research suggests.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineThis week in Zika: An anniversary, how the virus kills brain cells and more
New weapons in the fight against Zika, how the virus shrinks minibrains, a quick paper-based test for Zika, and more in this week’s Zika Watch.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Anthropology
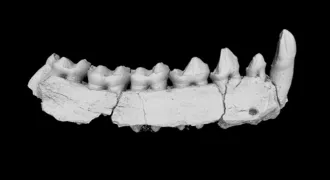
AnthropologyAsian primates hit hard by ancient climate change
Chinese fossils suggest primates diverged in Asia and Africa around 34 million years ago.
By Bruce Bower