Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Agriculture
AgricultureSuperbugs take flight from cattle farms
Winds can carry antibiotics and drug-resistant bacteria from cattle farms to downwind communities.
By Beth Mole -
 Anthropology
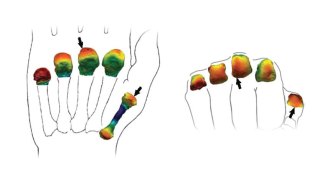
AnthropologyScans tell gripping tale of possible ancient tool use
South African fossils contain inner signs of humanlike hands, indicating possible tool use nearly 3 million years ago.
By Bruce Bower -
 Life
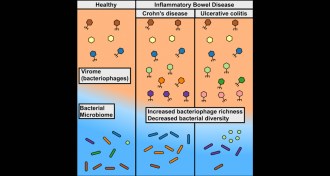
LifeWhen bacteria-killing viruses take over, it’s bad news for the gut
A rise in some bacteria-killing viruses in the intestines may deplete good bacteria and trigger inflammatory bowel diseases.
-
 Psychology
PsychologyEmotions go unnamed for some with eating disorders
A portion of women with eating disorders have a separate problem recognizing their own emotions, a condition called alexithymia.
By Bruce Bower -
 Environment
EnvironmentAtrazine’s path to cancer possibly clarified
Scientists have identified a cellular button that the controversial herbicide atrazine presses to promote tumor development.
By Beth Mole -
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyScrolls preserved in Vesuvius eruption read with X-rays
A technique called X-ray phase contrast tomography allowed scientists to read burnt scrolls from a library destroyed by the 79 A.D. eruption of Vesuvius.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBrain’s protective barrier gets leakier with age
Aging influences the breakdown of the blood-brain barrier, which may contribute to learning and memory problems later in life.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineImmune system ‘reset’ may give MS patients a new lease on life
With the help of their own stem cells, MS patients can stop the disease in its tracks in many cases.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Tech
TechUsing Facebook ‘likes,’ computer pegs people’s personalities
Using limited data from Facebook, computers can outdo humans in assessing a user’s openness, neuroticism and other personality traits.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyAttitude, not aptitude, may contribute to the gender gap
Does talent or hard work matter most? A new survey suggests an emphasis on genius predicts how many women end up in a field of study.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhat’s in a nap? For babies, it may make long-lasting memories
Taking naps after learning seems to help babies less than a year old make memories and keep them, for about a day anyway.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBrain’s plumbing may knock out blood test for brain injury
The brain's waste-removal system may complicate scientists' attempts to create a blood test to diagnose traumatic brain injury.