Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyTurkana Boy sparks row over Homo erectus height
Estimating the adult height and weight of an ancient youth from his skeleton has proven tricky.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHepatitis C treatment appears extremely effective
A mix of four medications has provided the most effective way to date to counter the hepatitis C virus in humans.
-
 Computing
ComputingApp could cut jet lag short
A new app calculates lighting schedules to help travelers adjust quickly to new time zones.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Life
LifeCommon lung infection suffocates with single protein
A Respiratory Syncytial Virus, or RSV, protein creates clumps of dead, bloblike lung cells.
By Beth Mole -
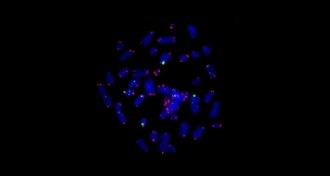 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineChanges in kids’ genomes linked to chronic stress
In a study of 40 nine-year-old boys, kids from underprivileged backgrounds had telomeres that were 19 percent shorter than those of boys from more privileged environments.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineIf your kid hates broccoli, try, try again
Repeated exposure to foods may be the antidote to picky eating.
-
 Humans
HumansFather’s obesity linked to autism in children
A father-to-be’s body mass may be a greater risk factor for his child’s development of autism than the body mass of the mother.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSurgery museum holds wonders for the brave
Anatomical displays sit alongside art depicting medical history at the International Museum of Surgical Science.
By Sid Perkins -
 Earth
EarthScience can save lives, but only if society lets it
Society faces lots of problems that science can’t yet fix. But there are also plenty of cases in which scientists know enough to avert tragedy.
By Eva Emerson -
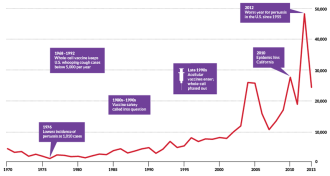 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhooping cough bounces back
A new type of pertussis vaccine introduced in the late 1990s may have led to the return of a disease that was nearly eradicated 40 years ago. Public opposition to vaccination hasn’t helped matters.
By Nathan Seppa -
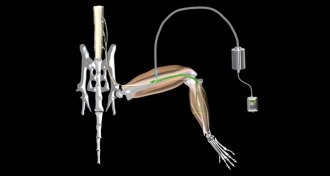 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceParalyzed mouse legs move with burst of light
Neural patch makes leg muscles twitch in paralyzed mice when blue light shines.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyBronze Age herders spread farming around Asia
Ancient seeds indicate that Central Asian animal raisers had an unappreciated impact on early agriculture.
By Bruce Bower