Humans
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyPeru’s Serpent Mountain sheds its mysterious past
No, aliens had nothing to do with a winding 1.5-kilometer-long path of holes. First used as a market, the Inca then repurposed it for tax collection.
By Bruce Bower -
 Artificial Intelligence
Artificial IntelligenceAs teens in crisis turn to AI chatbots, simulated chats highlight risks
From blaming the victim to replying "I have no interest in your life" to suicidal thoughts, AI chatbots can respond unethically when used for therapy.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineVolunteers agreed to be buried face-down in the snow, for science
A safety device helped maintain a buried person’s oxygen levels for up to 35 minutes, tests show, buying crucial time for an avalanche rescue.
-
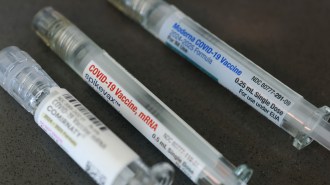 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCancer treatments may get a boost from mRNA COVID vaccines
Cancer patients who got an mRNA COVID vaccine within a few months of their immunotherapy lived longer than those who did not, health records show.
By Meghan Rosen -
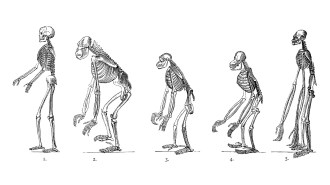 Anthropology
AnthropologyTwo tiny genetic shifts helped early humans walk upright
Scientists have linked bipedalism to changes in how the human pelvis developed millions of years ago.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyDNA reveals Neandertals traveled thousands of kilometers into Asia
DNA and stone tool comparisons suggest Eastern European Neandertals trekked 3,000 kilometers to Siberia, where they left a genetic and cultural mark.
By Bruce Bower -
 Humans
HumansNapoleon’s retreating army may have been plagued by these microbes
DNA from Napoleonic soldiers’ teeth uncovered two fever-causing bacteria that may have worsened the army’s fatal retreat from Russia.
By Meghan Rosen -
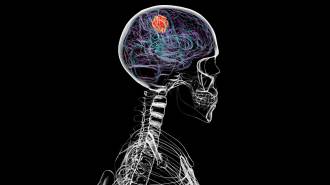 Humans
HumansBrain cancer can dissolve parts of the skull
Glioblastoma doesn't just affect the brain. It also erodes bones in the skull and changes the composition of immune cells in skull marrow.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Animals
AnimalsScientists and fishers have teamed up to find a way to save manta rays
Thousands of at-risk manta and devil rays become accidental bycatch in tuna fishing nets every year. A simple sorting grid could help save them.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMost women get uterine fibroids. This researcher wants to know why
Biomedical engineer Erika Moore investigates diseases that disproportionately affect women of color.
-
 Humans
HumansAn ancient bone recasts how Indigenous Australians treated megafauna
A new look at cuts on a giant kangaroo bone reveal First Peoples as fossil collectors, not hunters who helped drive species extinct, some scientists argue.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineCOVID-related smell loss may last years
Using a scratch-and-sniff test, researchers discovered that smell loss after COVID-19 may linger for more than two years.
By Meghan Rosen