Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Life
LifeAncient DNA shakes up the elephant family tree
DNA from straight-tusked elephant fossils is forcing scientists to reconsider the history of elephant evolution.
-
 Life
LifeLadybugs fold their wings like origami masters
Ladybug wings could lead to new foldable technologies.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineLive antibiotics use bacteria to kill bacteria
Certain bacteria will destroy other bacteria without harming humans. They may be an answer to antibiotic-resistant infections.
-
 Paleontology
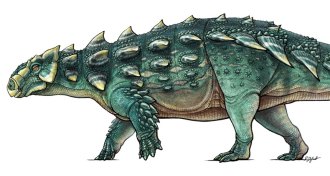
PaleontologyNew dinosaur resurrects a demon from Ghostbusters
The most complete skeleton of an ankylosaur shows an armored, club-tailed dinosaur with a head like a Ghostbusters demon.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineTherapy flags DNA typos to rev cancer-fighting T cells
Genetic tests help identify cancer patients who will benefit from immune therapy.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyPrimitive whales had mediocre hearing
Fossils suggest that early whale hearing was run-of-the-mill, along the same line as that of land mammals.
-
 Climate
ClimateClimate change might help pests resist corn’s genetic weapon
Rising temperatures may allow pests to eat corn that is genetically modified to produce an insect-killing toxin.
By Susan Milius -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineChoosing white or whole-grain bread may depend on what lives in your gut
Gut microbes determine how people’s blood sugar levels respond to breads.
-
 Animals
AnimalsBig slimy lips are the secret to this fish’s coral diet
A new imaging study reveals how tubelip wrasses manage to munch on stinging corals.
-
 Life
LifeWhen it comes to the flu, the nose has a long memory
Mice noses have specialty immune cells with long memories.
-
 Animals
AnimalsSooty terns’ migration takes the birds into the path of hurricanes
Sooty terns migrate south from southern Florida and back again. The track sometimes takes the birds into the path of hurricanes, a new study finds.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBrains encode faces piece by piece
Cells in monkey brains build up faces by coding for different characteristics.