Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceReaders intrigued by Mars’ far-out birth
Readers sent feedback on the Red Planet's formation, jumping genes and more
-
 Genetics
GeneticsDNA evidence is rewriting domestication origin stories
DNA studies are rewriting the how-we-met stories of domestication.
-
 Plants
PlantsHow to eavesdrop on kelp
Sounds reverberating through a kelp bed can be linked to environmental factors, suggesting a low-key way to monitor undersea communities.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsDouble-duty DNA plays a role in birth and death
Coronary artery disease may be the price humans pay for improved fertility.
-
 Animals
AnimalsThe blue wings of this dragonfly may be surprisingly alive
The wings of adult morpho dragonflies show tiny respiratory channels that may support a complex of nanostructures that shine blue.
By Susan Milius -
 Plants
PlantsPetunias spread their scent using pushy proteins
Scent molecules hitch a ride on a particular protein to escape flowers.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsHorse version of ‘Who’s your daddy?’ answered
Genetics and horse pedigrees reveal all modern domestic stallions’ sires.
-

-
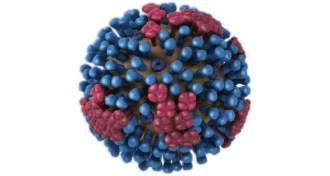 Life
LifeChronic flu patients could be an early warning system for future outbreaks
Cancer patients’ long-term flu infections may preview future viruses.
-
 Plants
PlantsFloral curve test shows what’s great for a moth is not so good for a flower
3-D printed flowers reveal a hidden conflict between a hawk moth and the flowers it pollinates.
By Susan Milius -
 Animals
AnimalsDrowned wildebeests can feed a river ecosystem for years
Only a small percentage of wildebeests drown as they cross the Mara River, but they provide resources for the river ecosystem for years after their deaths.
-
 Ecosystems
EcosystemsEarth’s dry zones support a surprising number of trees
A Google Earth-based estimate of dryland forests adds serious leafage to Earth’s total tree count.
By Beth Geiger