Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineReaders concerned about cancer’s sugary disguise
Tricky cancer cells, brain-shaping smartphones, a cow-burying badger and more in reader feedback.
-
 Climate
ClimateLakes worldwide feel the heat from climate change
Lakes worldwide are warming with consequences for every part of the food web, from algae, to walleye, to freshwater seals.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyFox experiment is replaying domestication in fast-forward
How to Tame a Fox recounts a nearly 60-year experiment in Russia to domesticate silver foxes.
-
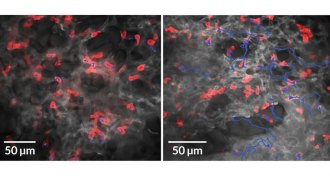 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineLungs enlist immune cells to fight infections in capillaries
Immune cells in the lungs provide a rapid counterattack to bloodstream infections, a new study in mice finds.
-
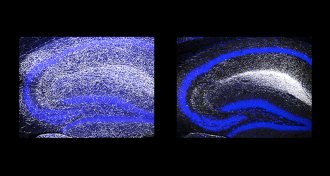 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceNerve cell miswiring linked to depression
A gene helps nerve cell axons extend to parts of the brain to deliver serotonin, a brain chemical associated with depression.
-
 Climate
ClimateOcean acidification may hamper food web’s nitrogen-fixing heroes
A new look at marine Trichodesmium microbes suggests trouble for nitrogen fixation in an acidifying ocean.
By Susan Milius -
 Genetics
GeneticsAncient DNA bucks tale of how the horse was tamed
DNA from ancient horses reveals early domestication involved plenty of stallions.
-
 Life
LifeHow a mushroom gets its glow
For the first time, biologists have pinpointed the compound that lights up in fungal bioluminescence.
By Susan Milius -
 Life
LifeHow a mushroom gets its glow
For the first time, biologists have pinpointed the compound that lights up in fungal bioluminescence.
By Susan Milius -
 Animals
AnimalsThe scales of the ocellated lizard are surprisingly coordinated
The mazelike patterns of the ocellated lizard’s skin follow a set of rules from computer science.
-
 Animals
AnimalsDog DNA study maps breeds across the world
Here are five findings from a massive study of dog breed genomes.
-
 Animals
AnimalsHow a dolphin eats an octopus without dying
An octopus’s tentacles can kill a dolphin — or a human — when eaten alive. But wily dolphins in Australia have figured out how to do this safely.