Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsGene knockouts in people provide drug safety, effectiveness clues
People naturally lacking certain genes give clues about drug safety and efficacy, a study in Pakistanis shows.
-
 Life
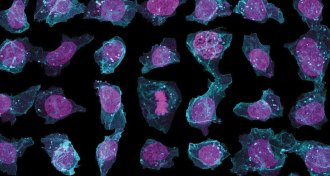
LifeCells’ stunning complexity on display in a new online portal
A new online explorer tool from the Allen Institute for Cell Science shows 3-D models of cell interiors.
-
 Climate
ClimateThe Great Barrier Reef is experiencing a major coral bleaching event right now
A second coral bleaching event has struck the Great Barrier Reef in 12 months, new observations reveal, raising concerns about the natural wonder’s future.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyBedbugs bugged prehistoric humans, too
Scientists have found the oldest known specimens of bedbug relatives in an Oregon cave system where ancient humans once lived.
-
 Humans
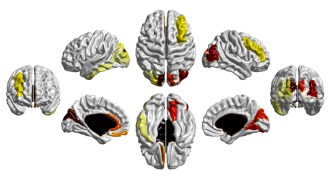
HumansScientists seek early signs of autism
The search for autism biomarkers, in the blood and the brain, is heating up.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineGenetic risk of getting second cancer tallied for pediatric survivors
Inherited mutations, not only treatment, affect the chances that a childhood cancer survivor will develop a second cancer later in life.
-
 Health & Medicine
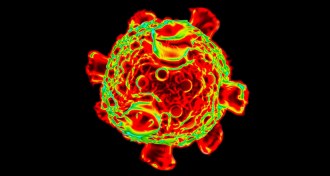
Health & MedicineCommon virus may be celiac disease culprit
A common virus may turn the immune system against gluten, leading to the development of celiac disease.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsCephalopods may have traded evolution gains for extra smarts
Editing RNA may give cephalopods smarts, but there’s a trade-off.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineReaders question mental health research
Maintaining mental health, protecting ocean critters and more in reader feedback.
-
 Life
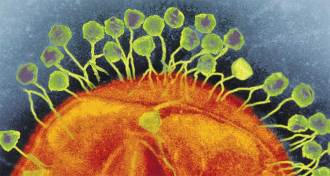
LifeCRISPR had a life before it became a gene-editing tool
Before it was a tool, CRISPR was a weapon in the never-ending war between microbes and viruses
By Rosie Mestel -
 Animals
AnimalsFirst fluorescent frogs might see each others’ glow
A polka dot frog, the first known fluorescent amphibian, may get a visibility boost in twilight and moonlight.
By Susan Milius -
 Science & Society
Science & Society‘Specimens’ goes behind the scenes of Chicago’s Field Museum
The Field Museum of Natural History in Chicago puts seldom-seen specimens on display in a new exhibit to highlight the crucial role of museum objects in scientific research.