Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Microbes
MicrobesMicrobe mix varies by kind of home
Urban homes hold more human-associated bacteria compared with rural homes. Subdivided houses with lots of rooms and poor ventilation could be to blame.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Genetics
GeneticsNeandertal DNA may raise risk for some modern human diseases
Neandertal DNA may once have helped humans, but now may contribute to disease.
-
 Animals
AnimalsAfrica’s poison arrow beetles are key in traditional hunting method
In the Kalahari of Namibia, some San people still hunt with a traditional method — arrows laced with poison taken from beetle larvae.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyIn all sorts of circumstances, life finds a way
Editor in Chief discusses the new marine habitats formed by human pollution and the alarming rise of the Zika virus.
By Eva Emerson -
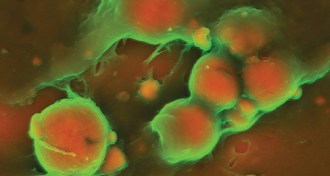 Life
LifeImages probe artery-hardening plaques
Zooming in on hardened arteries shows researchers which plaques pose heart attack risks.
-
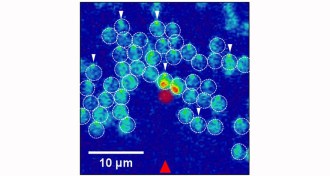 Microbes
MicrobesCyanobacteria use their whole bodies as eyeballs
Little spheres of cyanobacteria cells roughly focus light on sensitive compounds that let them walk in the right direction.
By Susan Milius -
 Earth
EarthOcean’s plastics offer a floating fortress to a mess of microbes
Microbes take up residence on ocean plastics, potentially causing changes in ocean environments.
-
 Agriculture
AgriculturePlants trick bacteria into attacking too soon
Scientists have discovered that a plant compound interferes with bacterial communication.
-
 Tech
TechThis roach-inspired robot can wiggle through tight spaces
Cockroaches inspired a compressible, crevice-navigating robot.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceCancer drug’s usefulness against Alzheimer’s disputed
A preliminary report questions the anti-Alzheimer’s activity of a cancer-fighting drug.
-
 Science & Society
Science & Society‘GMOs’ isn’t a four-letter word, but it is hard to define
The definition of what constitutes a genetically modified organism is a challenge to those tasked with developing standards for labeling foods that contain GMOs.
-
 Animals
AnimalsWhite-tailed deer have their own form of malaria
The otherwise well-studied white-tailed deer turns out to carry the first malaria parasite discovered in any deer.
By Susan Milius