Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & Medicine‘Vomiting device’ sounds gross but it helps study infections
Scientists created a “vomiting device” to study how norovirus spreads through the air.
-
 Life
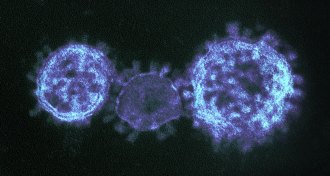
LifeExperimental MERS vaccine shows promise
An experimental vaccine against the MERS virus triggers immune protection, a new study finds.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Animals
AnimalsHummingbird tongues may work like micropumps
Hummingbird tongues work as elastic micropumps instead of simple thin tubes, researchers say in latest round of a scientific debate.
By Susan Milius -
 Animals
AnimalsAnother tiny frog species found in sky islands of Brazil
Another new species of miniature frog has been discovered amongst the leaf litter in the high cloud forests of southern Brazil.
-
 Microbes
MicrobesBacteria in flowers may boost honeybees’ healthy gut microbes
Honeybees may deliver doses of probiotics to the hive to help feed baby bees’ microbiome.
By Beth Mole -
 Chemistry
ChemistryThree kids’ science books offer fun, fascinating experiments
No matter what interests kids, there’s a do-it-yourself science book for them. Here are three with entertaining and educational options.
-
 Psychology
PsychologyBaby marmosets imitate parents’ sounds
Vocal learning may work similarly in marmoset monkeys, songbirds and humans.
By Bruce Bower -
 Chemistry
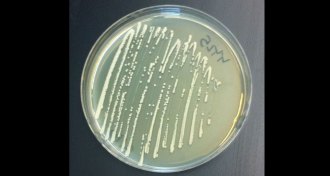
ChemistryPathway pieced together to make opiates in yeast
Scientists have engineered yeast to make sugar into thebaine, a precursor to opiates such as morphine.
-
 Animals
AnimalsA UFO would stress out a bear
Scientists need to know how animals, such as bears, react to the drones being used increasingly to study them.
-
 Animals
AnimalsLight pollution may disrupt firefly sex
Females of a common big dipper firefly weren’t as flashy when forced to flirt in LED light pollution.
By Susan Milius -
 Animals
AnimalsCougars may provide a net benefit to humans
Cougars have disappeared from the eastern United States. If they returned, they’d kill deer, preventing many car crashes, scientists find.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceShifting views of brain cells, and other fresh perspectives
The details emerging from the latest work on glial cells are sure to yield more insights as scientists continue their struggle to understand the mind.
By Eva Emerson