Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyMinutes after encountering danger, lemurs yawn
Madagascar primates yawn within minutes of encountering threats.
By Bruce Bower -
 Oceans
OceansEarth got first whiff of oxygen 3.2 billion years ago
Photosynthesis by early cyanobacteria pumped oxygen into Earth’s oceans 200 million years earlier than once thought, new geochemical analyses show.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyEarliest sea scorpion discovered in Iowa
Earliest sea scorpion discovered in impact crater in Iowa.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Animals
AnimalsA monkey uses a stick to pick its teeth and nose
A wild bearded capuchin monkey in Brazil was caught using tools to pick its nose and teeth.
By Erin Wayman -
 Animals
AnimalsRabbits leave a mark on soil long after they are gone
Twenty years after rabbits were removed from a sub-Antarctic island, soil fungus has yet to return to normal, a study finds.
-
 Animals
AnimalsSame math describes relationship between diverse predators and prey
From lions to plankton, predators have about the same relationship to the amount of prey, a big-scale ecology study predicts.
By Susan Milius -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHow farm life can prevent allergies
Farm dust prevents allergies by turning on an anti-inflammatory enzyme in the cells lining mice’s lungs.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Life
LifeUnhelpful adaptations can speed up evolution
Unhelpful changes in gene activity stimulate natural selection.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyNew dolphin fossil makes a splash
A newly discovered dolphin fossil provides clues to the evolution of river dolphins in the Americas.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyNew dolphin fossil makes a splash
A newly discovered dolphin fossil provides clues to the evolution of river dolphins in the Americas.
-
 Animals
AnimalsSome jellyfish sting deeper than others
A new study shows that some jellyfish have nematocysts that can sting deep into the skin. That may explain why their sting is so painful.
-
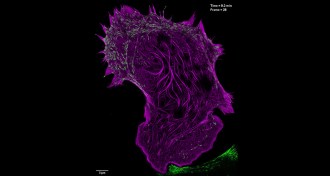 Life
LifeNew microscope techniques give deepest view yet of living cells
Two new microscopy techniques are helping scientists see smaller structures in living cells than ever glimpsed before.