Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBrain’s plumbing may knock out blood test for brain injury
The brain's waste-removal system may complicate scientists' attempts to create a blood test to diagnose traumatic brain injury.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceTo beat sleepiness of anxiety drugs, team looks to body’s clock
Studying basic functions, such as the body’s clock, has inadvertently led to a compound that relieves anxiety in mice.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceFeedback
Readers discuss volcanoes and brain studies involving chocolate, and recommend some science-based options for game night.
-
 Plants
PlantsTricky pitcher plants lure ants into a false sense of security
Carnivorous pitcher plants exploit social lives of ants as scouts escape and inadvertently lead nest mates to death trap.
By Susan Milius -
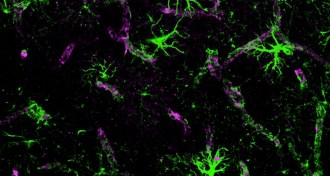
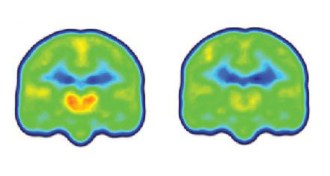 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceProtectors of our nervous system play a role in pain
PET and MRI brain scans show that the cells that protect our central nervous system also play a role in chronic pain.
-
 Animals
AnimalsSquids edit genetic directions extensively
In squids, RNA editing means that DNA often does not get the final say in which proteins are created.
-
 Animals
AnimalsPaternity test reveals father’s role in mystery shark birth
A shark pup was born in a tank with three female sharks but no males. A genetic study finds that the shark must have stored sperm for nearly four years.
-
 Animals
AnimalsAmazonian bird may act the part of its hairy caterpillar disguise
A rare view of a baby cinereous mourner feeds debate over whether the bird both looks and acts the part of a toxic hairy caterpillar as defense against predators.
By Susan Milius -
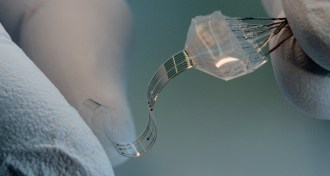 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceSoft brain implant helps paralyzed rats walk again
Scientists have made a soft, flexible electrical implant that mimics the elasticity of the brain and spine's protective tissue.
-
 Animals
AnimalsDisco clams may flash chemical-weapons warning
Puzzling disco clam light show might warn predators not to bite.
By Susan Milius -
 Climate
ClimateGalápagos waters preview future for corals
Posthumous analysis of Galápagos coral reefs reveals how climate change, carbon dioxide and pollution could kill off reefs worldwide by 2050.
By Beth Mole -
 Animals
Animals‘Bag of chips effect’ helps bats find a meal
Bats get a clue to where dinner is by listening to peers attacking prey.