Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Animals
AnimalsHow a spider spins electrified nanosilk
The cribellate orb spider (Uloborus plumipes) hacks and combs its silk to weave electrically charged nanofibers, a new study suggests.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceChicks show left-to-right number bias
Recently hatched chicks may have their own version of the left-to-right mental number line.
By Susan Milius -
 Genetics
GeneticsPregnancy in mammals evolved with help from roving DNA
DNA that “jumped” around the genome helped early mammals shift from laying eggs to giving birth to live young.
-
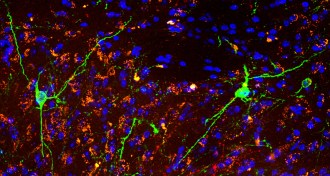 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceNewly identified brain circuit could be target for treating obesity
In mice, specific nerve cells control compulsive sugar consumption, but not normal feeding, hinting at a new therapeutic target for treating obesity.
-
 Plants
PlantsPlant chemical weaponry may offer ammunition for pesticides
Chemicals produced by two plant species disrupt insect hormone pathways and could be developed in to efficient, safe pesticides.
-
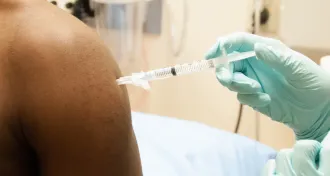 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineEbola vaccine performs well in U.K. human trial
A vaccine that protects against the Zaire strain of Ebola turns in promising preliminary results from a human trial.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietySmell circuitry, stalled stem cells and more reader feedback
Readers discuss a journal's publishing practices, ask about the human sense of smell and weigh in on their favorite picks from our Top 25 stories of the year.
-
 Animals
AnimalsHighway bridge noise disturbs fish’s hearing
In the lab, blacktail shiners had trouble hearing courtship growls over Alabama bridge traffic recordings.
By Susan Milius -
 Animals
AnimalsAnt-eating bears help plants
A complex web of interactions gives a boost to rabbitbrush plants when black bears consume ants.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceImmune system may remember and adapt to stress
Mice without immune systems who receive stressed immune cells are less anxious and more social, suggesting that the immune system can adapt to stress.
-
 Animals
AnimalsChameleon tongue power underestimated
A South African chameleon species can shoot its tongue with up to 41,000 watts of power per kilogram of muscle involved, a new study finds.
By Susan Milius -
 Ecosystems
Ecosystems‘Earth: A New Wild’ puts people in the picture
PBS nature series ‘Earth: A New Wild’ shows humans living with, and not off, their environments