Life
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Psychology
PsychologyHypothesis on evolution of PMS attracts hostility
A new hypothesis states that PMS is evolutionarily useful for making women leave an infertile partnership. But other scientists question whether the hypothesis is reasonable or, in fact, even necessary.
-
 Animals
AnimalsBumphead parrot fish declare their arrival with a crunch
Months of swimming with the coral-biter bumpheads exposes the animal’s extreme digestion and also a conservation dilemma.
By Susan Milius -
 Life
LifeNew gut-dwelling virus is surprisingly common
It’s not clear yet whether the bacteriophage crAssphage, found in people’s intestines, has any health effects.
-

-
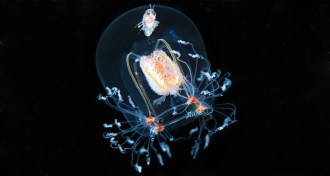 Animals
AnimalsSeeing past the jellyfish sting
Jellies don’t get nearly as much love as their cousins, the corals, but they deserve credit for providing homes to some creatures, dinner to others and more. They’re an integral part of the oceans.
By Susan Milius -
 Life
LifeTest drug stops Marburg virus in monkeys
Using a nano-size piece of RNA, scientists have stopped Marburg virus in monkeys.
-
 Animals
AnimalsThese lizards may be able to learn from each other
An experiment with skinks provides the first evidence of social learning in lizards.
-
 Oceans
OceansViruses might tame some algal blooms
The rapid demise of a giant, carbon-spewing algal bloom points to the influence of viral wranglers.
-
 Animals
AnimalsHummingbirds evolved a strange taste for sugar
While other birds seem to lack the ability to taste sugar, hummingbirds detect sweetness using a repurposed sensor that normally responds to savory flavors.
-
 Ecosystems
EcosystemsLake under Antarctic ice bursts with life
Abundant microbes thrive in subglacial lakes deep under the Antarctic ice sheet.
-
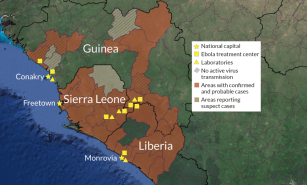 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineExperimental drugs and vaccines poised to take on Ebola
The use of experimental drugs and vaccines against Ebola may turn the tide against an outbreak in Africa that has defied efforts to control it.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Animals
AnimalsOrcas and other animals may speak with complexity
From finches to orangutans, animal vocalizations may be more complex and not as distant from the structure of human language as previously thought.