Neuroscience
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceStudy linking narcolepsy to autoimmunity retracted
Data linking disorder to immune cells couldn’t be replicated, scientists say.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceHippocampus may help homing pigeons explore
When researchers remove pigeons’ hippocampi, birds fly straighter on early parts of journey home.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineLong-term Parkinson’s treatment sheds bad rep
Prolonged used of levodopa doesn’t increase the severity of side effects from the Parkinson’s drug, new research shows.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceFor rats, a break from stress isn’t worth the relief
An unplanned vacation from stress might seem like a good idea, but a new study in rats shows that unpredictable escapes from pressure produce more strain on the first day back.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsHints about schizophrenia emerge from genetic study
From thousands of genomes, researchers pinpoint dozens of DNA changes that may underlie schizophrenia
-
 Animals
AnimalsTermite soldiers locate battles with vibrational clues
To locate invasions, termite soldiers listen for millisecond-long delays in vibrational distress signals sent out by other soldiers.
By Susan Milius -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceObese women struggle to learn food associations
In a lab experiment, women fail to connect color signal with tasty reward, a deficit that may contribute to obesity.
-
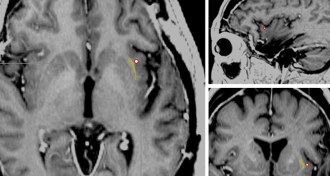 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceElectrode turns consciousness on and off
Woman lost awareness, though appeared awake, when her brain was stimulated near an area called the claustrum.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceIn female flies, sex is more complex than yes or no
A female fruit fly’s role in mating has appeared to be a simple yes or no. But now three new papers show the behavior is far more subtle, and intricate, than first thought.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceHeavy marijuana use may affect dopamine response
People who regularly smoke five joints a day had dampened reactions to the chemical messenger dopamine.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceFeedback
Readers weigh in on marijuana legalization, twisted twists, high-kicking frogs and more.
-
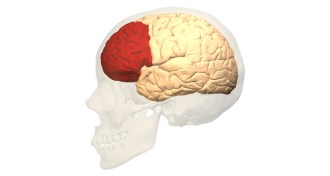 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceMRI scans reveal how the brain tells the body to pee
Scientists see heightened brain activity in men right before they urinate.