Physics
Sign up for our newsletter
We summarize the week's scientific breakthroughs every Thursday.
-
 Materials Science
Materials ScienceQuestions about toxic red tides, and more reader feedback
Readers had inquiries about a new deicing material, harmful algal blooms and more.
-
 Physics
PhysicsA new measurement bolsters the case for a (slightly) smaller proton
The PRad physics experiment has come up with a result favoring a punier proton.
-
 Physics
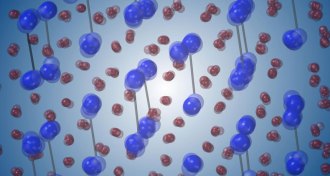
PhysicsVanadium dioxide’s weird phase transition just got weirder
When shifting from one crystalline structure to another, the atoms inside vanadium dioxide bumble around a lot more than expected.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyThree gas clouds nearly grazed the edge of the Milky Way’s black hole
Gas clumps cozy up to the Milky Way’s enormous black hole, new observations reveal.
-
 Physics
PhysicsThis cloud-zapping laser could help scientists create a quantum internet
A powerful fast-pulsing laser can bust through clouds to make quantum communication via satellite easier.
-
 Particle Physics
Particle PhysicsWhat the electron’s near-perfect roundness means for new physics
The electron remains stubbornly round, meaning we may need to build beyond the Large Hadron Collider to find physics outside of the standard model.
-
 Cosmology
CosmologyThe universe’s continued existence implies extra dimensions are tiny
The strictest limits yet on the size of extra dimensions come from the fact that black holes haven't destroyed the universe.
-
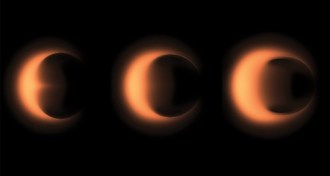 Astronomy
Astronomy‘Einstein’s Shadow’ explores what it takes to snap a black hole’s picture
The new book offers a behind-the-scenes look at the Event Horizon Telescope’s attempt to image a black hole.
-
 Physics
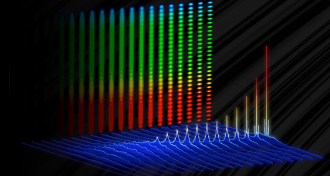
PhysicsA new ultrafast laser emits pulses of light 30 billion times a second
A new technique allows lasers to pulsate at a higher rate than ever before.
-
 Particle Physics
Particle PhysicsPhysicist Leon Lederman, renowned for his subatomic particle work, has died
The Nobel Prize–winning particle physicist discovered multiple particles and wrote popular science books.
-
 Physics
PhysicsDazzling laser feats earn these physicists a Nobel
The 2018 Nobel Prize in physics went to scientists — including the third-ever female winner — who made optical tweezers and boosted the strength of laser pulses.
-
 Physics
PhysicsGroundbreaking ways of manipulating light win trio the 2018 physics Nobel
Three scientists, including the third woman to win a physics Nobel, are honored for their laser inventions.