All Stories
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyFor the first time, astronomers saw dust in space being pushed by starlight
Images collected over 16 years reveal that dust expelled from a well-known binary star system is hurried on its way by light from those stars.
-
 Psychology
PsychologyThe pandemic shows us how crises derail young adults’ lives for decades
Age matters for when we experience calamities, such as pandemics. Young adults are especially vulnerable to getting thrown off their life course.
By Sujata Gupta -
 Animals
AnimalsHoneybees order numbers from left to right, a study claims
In experiments, bees tend to go to smaller numbers on the left, larger ones on the right. But the idea of a mental number line in animals has critics.
-
 Animals
AnimalsSome seabirds survive typhoons by flying into them
Streaked shearwaters off the coast of Japan soar for hours near the eye of passing cyclones as a strategy to weather the storm.
By Freda Kreier -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA swarm of sneaky omicron variants could cause a COVID-19 surge this fall
Scientists are tracking similar mutations showing up in many variants that help the coronavirus evade some of our immune defenses and treatments.
-
 Earth
Earth50 years ago, scientists found a new way to clean up oil spills
In the 1970s, researchers added chemicals to the list of oil spill cleanup methods. Soon, they may add microbes.
By Meghan Rosen -
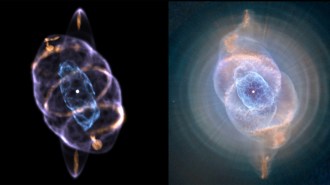 Astronomy
AstronomyA 3-D model of the Cat’s Eye nebula shows rings sculpted by jets
The Cat’s Eye is one of the most complex nebulae known. A 3-D reconstruction reveals the source of some of that complexity.
-
 Life
LifeThis ancient worm might be an important evolutionary missing link
A roughly 520-million-year-old fossil may be the common ancestor of a diverse collection of marine invertebrates.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyDrone photos reveal an early Mesopotamian city made of marsh islands
Urban growth around 4,600 years ago, near what is now southern Iraq, occurred on marshy outposts that lacked a city center.
By Bruce Bower -
 Paleontology
PaleontologyDinosaur ‘mummies’ may not be rare flukes after all
Bite marks on a fossilized dinosaur upend the idea that exquisite skin preservation must result from a carcass's immediate smothering under sediment.
By Jake Buehler -
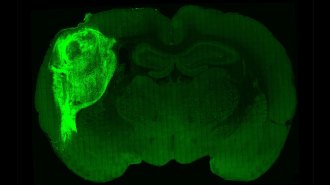 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceClumps of human nerve cells thrived in rat brains
New results suggest that environment matters for the development of brain organoids, 3-D nerve cell clusters that grow and mimic the human brain.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceNASA’s DART mission successfully shoved an asteroid
Data obtained since the spacecraft intentionally crashed into an asteroid show that the impact altered the space rock’s orbit even more than intended.