All Stories
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceCosmic dust may create Mars’ wispy clouds
Magnesium left by passing comets seeds the clouds of Mars, a new study suggests.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBrain waves may focus attention and keep information flowing
Not just by-products of busy nerve cells, brain waves may be key to how the brain operates.
-
 Animals
AnimalsDino-bird had wings made for flapping, not just gliding
Archaeopteryx fossils suggest the dino-birds were capable of flapping their wings in flight.
-
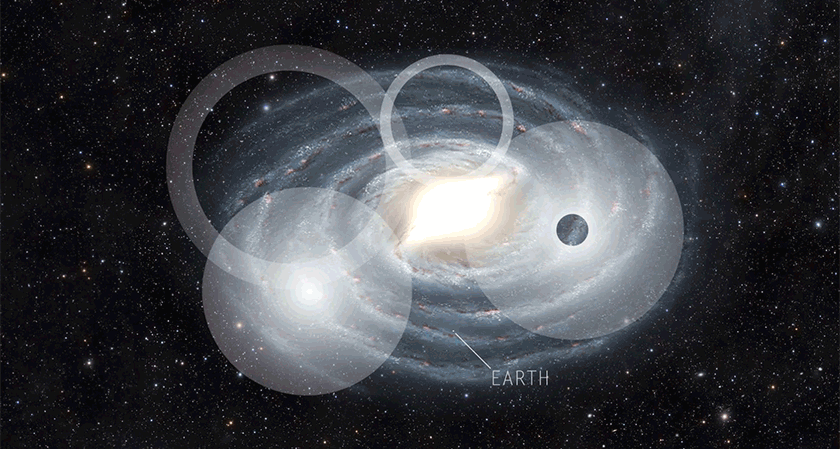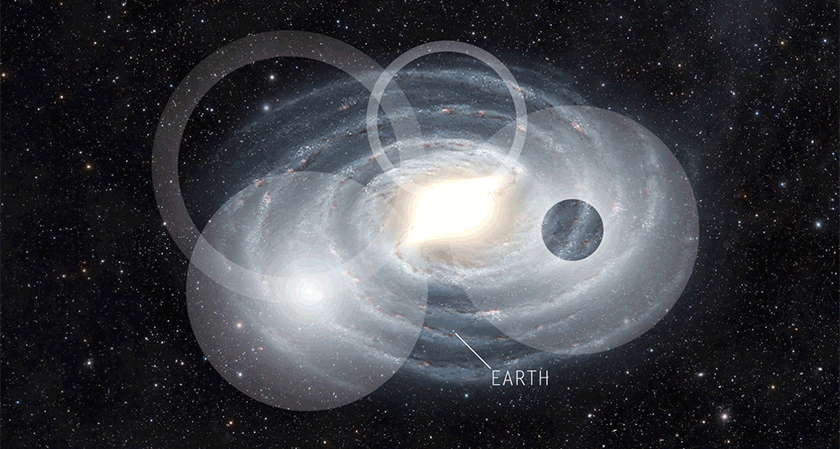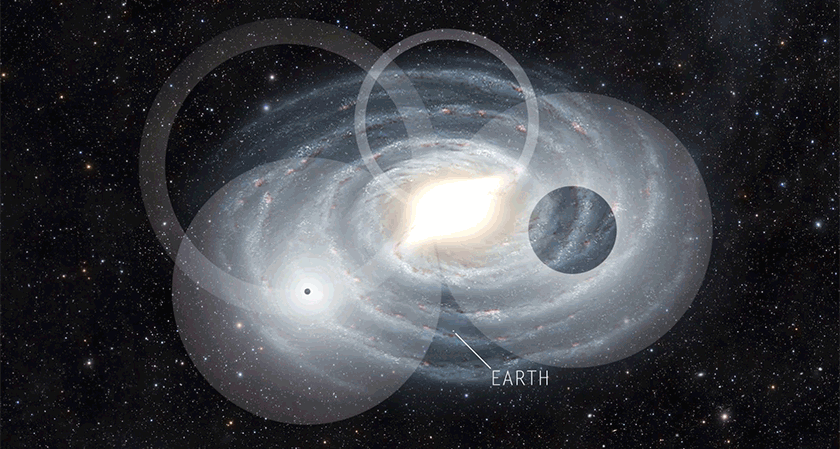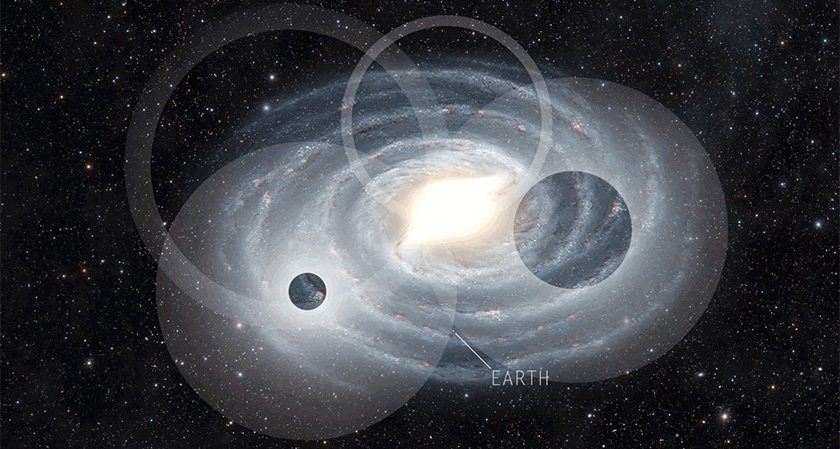 Astronomy
AstronomyWe probably won’t hear from aliens. But by the time we do, they’ll be dead.
Astronomers build on the Drake Equation to probe the chance that humans will find existing aliens. The answer: Not likely.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceHow biology breaks the ‘cerebral mystique’
The Biological Mind rejects the idea of the brain as the lone organ that makes us who we are. Our body and environment also factor in, Alan Jasanoff says.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceDepression among new mothers is finally getting some attention
Scientists search new mothers’ minds for clues to postpartum depression.
By Laura Beil -
 Quantum Physics
Quantum PhysicsSuperconductors may shed light on the black hole information paradox
Materials that conduct electricity without resistance might mimic black hole physics.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyWhat we do and don’t know about how to prevent gun violence
Background checks work to prevent gun violence; concealed carry and stand-your-ground laws don’t. But lack of data makes it hard to make other links.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyMuseum mummies sport world’s oldest tattoo drawings
A wild bull and symbolic designs were imprinted on the bodies of two Egyptians at least 5,000 years ago.
By Bruce Bower -
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyDiscussing what matters when facts are not enough
Editor in Chief Nancy Shute reflects on finding common ground with science and policy.
By Nancy Shute -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceReaders muse about memory, magnetic monopoles and more
Readers had questions about the physical trace of memory, magnetic monopoles, blowflies and more.
-
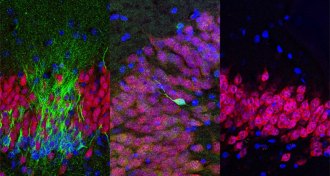 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceThe debate over how long our brains keep making new nerve cells heats up
Adult humans don’t have newborn nerve cells in a memory-related part of the brain, a controversial paper suggests.