All Stories
-
 Genetics
GeneticsProtective genetic variant may offer a path to future autoimmune therapies
A natural tweak in the TYK2 protein strikes a balance between weak and overactive immune systems.
-
 Physics
PhysicsUnits of measure are getting a fundamental upgrade
New units based on fundamental properties of the universe will make measurements more precise.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceEyes offer window into brain’s timekeepers
In new experiments of time perception, when pupils were large, monkeys underestimated a second.
-
 Earth
EarthMount St. Helens is a cold-hearted volcano
Geophysics reveals that deep beneath Mount St. Helens, there’s no source of hot magma, just a wedge of cold serpentinite rock. Where is the missing heat?
By Beth Geiger -
 Earth
EarthThe southern San Andreas has a smaller, neighboring fault to its west
The newly-discovered Salton Trough Fault runs parallel to the southern San Andreas Fault in California, potentially affecting the region’s earthquake risk.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyFirst known fossilized dinosaur brain unearthed, scientists claim
A dinosaur fossil that preserves brain tissue has been discovered for the first time, researchers announce.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineRiding roller coasters might help dislodge kidney stones
Researchers took a 3-D printed kidney containing tiny stones and urine for a spin on a roller coaster and found their patients’ stories of kidney stones passing on the ride to have merit.
By Laura Beil -
 Psychology
PsychologyLearning curve not so smooth
Preschoolers tend to reach a milestone of social thinking after months of fits and starts.
By Bruce Bower -
 Earth
Earth‘A Most Improbable Journey’ offers scientific take on human history
Walter Alvarez’s “A Most Improbable Journey” gives readers a tour of “Big History,” linking human history to unpredictable cosmic, geologic and biological events.
-
 Paleontology
PaleontologyPicture of primate common ancestor coming into focus
A new family tree analysis predicts behavior of primate common ancestor.
By Erin Wayman -
 Paleontology
PaleontologyEarly birds could achieve liftoff
Early birds and other flying dinosaurs had the strong legs and wing speed needed to launch into the air directly from the ground, researchers argue.
By Meghan Rosen -
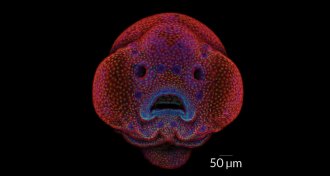 Life
LifeHow to make a fish face, and other photo contest winners
The tiny face of a 4-day-old zebrafish embryo snags the top spot in microscopy photography contest.