All Stories
-
 Animals
AnimalsDocumentary looks for meaning in Koko the gorilla’s life
'Koko — The Gorilla Who Talks' documents the nearly 45-year relationship between researcher Penny Patterson and Koko, the subject of an ape sign language project.
By Erin Wayman -
 Health & Medicine
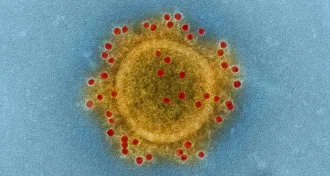
Health & MedicineHow one patient spread MERS to 82 people
One person passed the Middle East respiratory syndrome virus to 82 others during an outbreak in South Korea in 2015.
-
 Climate
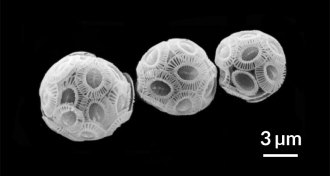
ClimatePhytoplankton’s response to climate change has its ups and downs
In a four-year experiment, the shell-building activities of a phytoplankton species underwent surprising ups and downs.
-
 Life
LifeMini ‘wind farm’ could capture energy from microbes in motion
Bacteria could spontaneously organize and rotate turbines, computer simulations show.
-
 Oceans
OceansUnderwater city was built by microbes, not people
Submerged stoneworklike formations near the Greek island of Zakynthos were built by methane-munching microbes, not ancient Greeks.
-
 Life
LifeHightailing it out of the water, mudskipper style
A robot and a land-walking fish show how a tail might have made a huge difference for early vertebrates conquering the slippery slopes of terrestrial life.
By Susan Milius -
 Tech
TechLight-activated heart cells help guide robotic stingray
Layers of silicone, gold and genetically engineered rat heart cells make up the body of a new stingray robot that can swim in response to light.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Life
LifeArtificial hearing has come a long way since 1960s
Scientists envisioned artificial hearing 50 years ago. Today, they are working to make it superhuman.
-
 Life
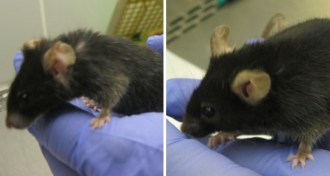
LifeDonor mitochondria could influence metabolism, aging
Mitochondrial DNA donation could have unexpected long-term health consequences for “three-parent babies.”
-
 Animals
AnimalsTo zip through water, swordfish reduce drag
A newly discovered oil-producing organ inside the swordfish’s head gives the animal slick skin to swim faster.
-
 Animals
AnimalsLionfish invasion comes to the Mediterranean
Scientists had thought that the Mediterranean was too cold for lionfish to permanently settle there. But now they’ve found a population of the fish off Cyprus.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryNuclear bomb debris can reveal blast size, even decades later
Measuring the relative abundance of various elements in debris left over from nuclear bomb tests can reveal the energy released in the initial blast, researchers report.