All Stories
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHaving parasites can boost fertility
Infection with parasitic worms tinkers with fertility.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Animals
AnimalsAdorable birds tap dance their way into the heart of a mate
Blue-capped cordon-bleu songbirds not only sing, but also tap dance to woo mates, study reveals.
-
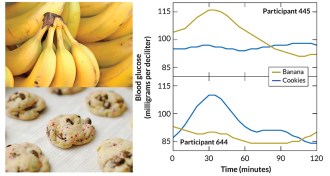 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA good diet for you may be bad for me
Eating the same foods can produce very different reactions in people.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceWay-out world is solar system’s most distant object — for now
An icy world over 15 billion kilometers from the sun is the new record holder for most distant object in the solar system.
-
 Animals
AnimalsVampire bats share blood to make friends
Vampire bats that share blood with nonrelatives have a wider social network to rely on when they’re in need, a new study finds.
-
 Animals
AnimalsGetting creative to cut methane from cows
Changing feed, giving vaccines and selective breeding may enable scientists to help beef and dairy cattle shake their title as one of society's worst methane producers.
By Laura Beil -
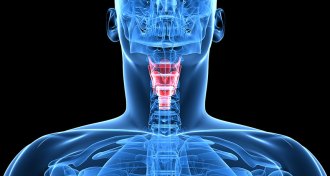 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineEngineered vocal cords show promise in animal tests
Lab-grown vocal cord tissue could lead the way to better treatments for people with vocal problems
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceGlimpse of baby planet shows what to expect when a star is expecting
A baby planet is still growing in the disk of gas that encircles a young star.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyThe vagus is the nerve to know
The nervous system's meandering superhighway has the potential to lead researchers treatments for myriad health conditions.
By Eva Emerson -
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceBright minds, antineutrinos and more reader feedback
In the November 28, 2015, issue of Science News, readers discussed humanizing science, frog mating calls, antineurtrinos and Martian dust storms.
-
 Psychology
PsychologyCulture shapes sense of fairness
Culture shapes kids’ sense of fairness, especially when they get the short end of the stick.
By Bruce Bower -
 Life
LifeTruffles aren’t laced with radioactive cesium
Fallout from the Chernobyl disaster hasn’t made truffles dangerously radioactive, scientists find.