All Stories
-
 Animals
AnimalsPonds and their toads cured of dreaded disease
Treating both tadpoles and their ponds for infection by deadly Bd chytrid fungus lets midwife toads go wild again.
By Susan Milius -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineWhen selenium is scarce, brain battles testes for it
In competition for selenium, testes draw the nutrient away from the brain.
-
 Psychology
PsychologyCaffeine gives cocaine an addictive boost
Not only is it popular to “cut” cocaine with caffeine, the combination might be more addictive.
-
 Plants
PlantsGenetic battle of the sexes plays out in cukes and melons
Genetics reveals new approach to preventing inbred seeds and encouraging more fruitful crops.
By Susan Milius -
 Animals
AnimalsHungry elephants turn trunks into leaf blowers
Darwin once observed an elephant using its trunk to blow an object closer. Japanese zoo elephants use the behavior to obtain food, a new study reports.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineStudy brews up more evidence for coffee’s health benefits
Drinking up to five cups of coffee a day reduced the risk of dying early from heart and brain diseases and suicide.
-
 Plants
PlantsAncient gardeners saved the gourd
Domestication might have helped early vine plants like pumpkin survive after seed-dispersing megafauna went extinct.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineStudy brews up more evidence for coffee’s health benefits
Drinking up to five cups of coffee a day reduced the risk of dying early from heart and brain diseases and suicide.
-
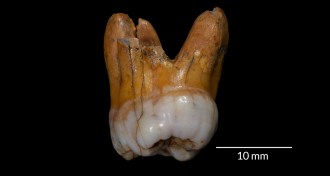 Anthropology
AnthropologyDNA puts Neandertal relatives in Siberia for 60,000 years
Recovered DNA suggests Denisovans inhabited Siberia for around 60,000 years.
By Bruce Bower -
 Plants
PlantsAncient gardeners saved the gourd
Domestication might have helped early vine plants like pumpkin survive after seed-dispersing megafauna went extinct.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyDNA puts Neandertal relatives in Siberia for 60,000 years
Recovered DNA suggests Denisovans inhabited Siberia for around 60,000 years.
By Bruce Bower -
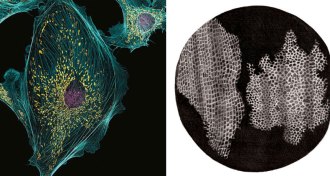 Life
LifeMicroscopes have come a long way since 1665
A 350-year-old drawing in Robert Hooke’s Micrographia and an award-winning photo demonstrate the evolution of the microscope.
By Andrew Grant