All Stories
-
 Archaeology
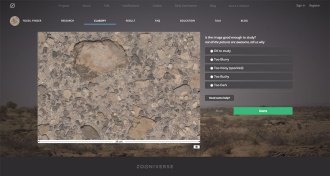
ArchaeologySearch for fossils from the comfort of home
The citizen science website FossilFinder.org lets anyone with an Internet connection look for fossils and characterize rocks at Kenya’s Lake Turkana Basin
By Erin Wayman -
 Earth
EarthPioneering geologist sought to demystify volcanic eruptions
In The Last Volcano, a geologist profiles Thomas Jaggar, one of the 20th century’s most influential volcanologists.
By Sid Perkins -
 Animals
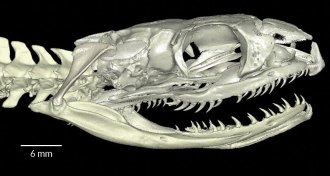
AnimalsSnakes evolved from burrowing ancestor, new data suggest
A new X-ray analysis of inner ears is the latest to weigh in on whether modern snakes descended from a burrowing or a swimming reptile.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Animals
AnimalsMystery deepens for what made tarantulas blue
Blue hair on tarantulas shows what evolution does with iridescence that females probably don’t care about.
By Susan Milius -
 Planetary Science
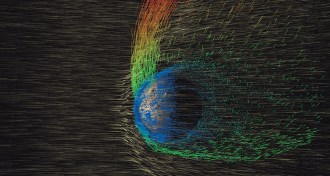
Planetary ScienceA defenseless Mars is losing its atmosphere
Measurements of Mars’ atmosphere leaking into space could help scientists explain how the Red Planet lost its once life-friendly climate.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyMystery still surrounds Neandertals
Neandertals’ relationship to modern humans is still a matter of debate.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyMore mysterious extragalactic signals detected
Five more fast radio bursts from other galaxies have shown up and one of them is a double.
-
 Animals
AnimalsFor a python, every meal is like Thanksgiving
Burmese pythons rarely eat, but when they do, they gorge. Unlike humans, pythons have adaptations that allow them to survive on huge meals.
-
 Genetics
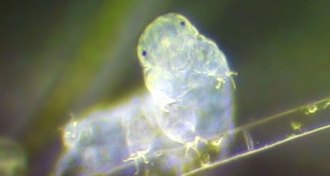
GeneticsWater bears are genetic mash-ups
Drying out may help tardigrades soak up new DNA, which in turn aids the water bears in withstanding stress.
-
 Life
LifeDNA doubled in conifer ancestors
The genomes of conifers — pine, cypress and yew trees — doubled twice in the distant past.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceTaste is all in your head
By targeting certain nerve cells in a mouse’s brain, scientists made plain water turn bitter or sweet.
-
 Physics
PhysicsFinal chapter published in decades-long Gravity Probe B project
It took more than 50 years, but an experiment testing general relativity has finally come to a close.
By Andrew Grant