All Stories
-
 Animals
AnimalsOctopuses can ‘see’ with their skin
Eyes aren’t the only cephalopod body parts with light-catching molecules.
By Susan Milius -
 Materials Science
Materials ScienceLike a balloon, peculiar magnet grows and shrinks
A recently discovered alloy of iron and gallium can expand and contract like a balloon when exposed to a magnetic field.
By Andrew Grant -
 Animals
AnimalsRising temperatures may cause problems for cold-blooded critters
Ectotherms cannot easily handle extreme temperatures, a new study finds.
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyEarliest known stone tools unearthed in Kenya
East African discoveries suggest stone-tool making started at least 3.3 million years ago.
By Bruce Bower -
 Astronomy
AstronomyPeeks into early life of supernovas show how to blow up a star
Multiple supernovas show off some of the ways a star can explode.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyGene therapy, Gattaca-style, poses ethical issues
Gene therapy becomes more sophisticated, and the debate over the ethics of DNA tinkering grows.
By Eva Emerson -
 Paleontology
PaleontologySuds versus nanoparticles and more reader feedback
Readers discuss the posture of an ancient reptile and why washing machines and nanoparticles don't mix.
-
 Animals
AnimalsCrows safeguard sticks to speed future food-finding forays
New Caledonian crows safeguard the sticks they use to find food. As the risk of losing the tool increases, the more protective the birds become.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicinePlaytime at the pool may boost youngsters’ bodies and brains
Learning to swim early in life may boost kids’ learning in language and math.
-
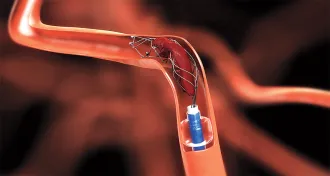 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineSnagging blood clots upgrades stroke care
A new device threaded up to the brain via catheter can unblock vessels in cerebral arteries, studies show.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceSea salt may stripe Europa’s surface
Salt deposits on Jupiter’s moon Europa might be responsible for brown stripes on the icy satellite’s surface.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBroken bones heal with young blood, how remains a mystery
Blood from young mice rejuvenates bones of elderly mice, but how it works remains a mystery.
By Meghan Rosen