All Stories
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineOne in 10 people with tattoos experience rashes, scarring or other problems
Tattoos carry risk of long-term rash; red ink may be most irritating color.
By Meghan Rosen -
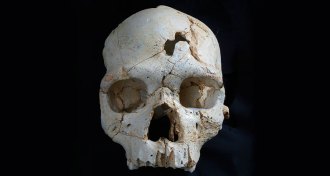 Anthropology
AnthropologyDouble blow to skull is earliest evidence of murder, a 430,000-year-old whodunit
A 430,000-year-old hominid skull shows signs of murder, making it the earliest suspected homicide.
By Julia Rosen -
 Humans
HumansFossils suggest another hominid species lived near Lucy
Fossil jaws dating to over 3 million years ago may add a new species to the ancient hominid mix.
By Bruce Bower -
 Animals
AnimalsWild dogs cause problems for people in Nepal
The endangered dhole has a reputation for killing livestock, but its taste for blue sheep could also be an issue, a new study finds.
-
 Climate
ClimateEverest could lose most of its ice by the end of the century
Glaciers around Mt. Everest will lost most of their ice by the end of the century, new research predicts.
-
 Climate
ClimateEverest could lose most of its ice by 2100
The Everest region of the Himalayas could lose 73 to 96 percent of its ice by 2100, new research predicts.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceNASA picks nine instruments for future mission to Europa
NASA has selected nine instruments to fly on a future spacecraft to Jupiter’s ice-covered moon Europa.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsWhite House hits pause on editing human germline cells
The White House has hit pause, for now, on clinical experiments that could alter the human germ line.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceDiet and nutrition is more complex than a simple sugar
A new study shows that fructose may leave you wanting more when compared to the same dose of glucose. But in studies of single nutrients, it’s important to be cautious.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsGenes and environment balance each other
Genes and environment have equal influence on human traits.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyBrightest galaxy discovered
The brightest known galaxy is about 350 trillion times as bright as the sun, and a supermassive black hole is to blame.
-
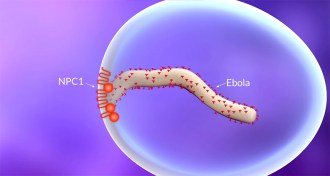 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineEbola gatekeeper protein identified
Ebola’s ability to infect appears to depend on a key transport protein that guides the virus into cells.
By Meghan Rosen