All Stories
-
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyTelling stories from stone tools
Existing stone tool categories may hide more than they reveal. New methods for analyzing stone artifacts aim to better reconstruct how hominids interacted and moved across Africa, Asia and Europe.
By Bruce Bower -
 Animals
AnimalsPiggyback rides and other crocodile fun
We don’t know the playful side of crocodiles perhaps only because we haven’t looked.
By Susan Milius -
 Quantum Physics
Quantum PhysicsQuantum links provide clues to causation
Quantum entanglement enables physicists to determine cause and effect just by tracking the association between two measurements.
By Andrew Grant -
 Tech
Tech‘Rust’ chronicles humankind’s incessant battle with corrosion
‘Rust’ recounts humanity’s unending battle against corrosion, which each year costs the United States an estimated $437 billion — more than all natural disasters combined.
By Sid Perkins -
 Anthropology
Anthropology‘The Invaders’ sees dogs as key to modern humans’ success
Neandertals went extinct when Homo sapiens transformed wolves into hunting aids, author proposes.
By Bruce Bower -
 Climate
ClimateRain slows whipping hurricane winds
Taking raindrop drag into account — which may slow hurricane winds by as much as 30 percent — could help improve hurricane forecasts.
-
 Climate
ClimateWinter storms 24 times as deadly as estimated
By ignoring car and plane crashes related to bad weather, U.S. tallies of winter storm deadliness severely underestimate hazard.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomySolo planets may be surprisingly common
Rogue planets may form as stars do, but on a smaller scale, or they may go forced out of orbit during planetary ping-pong. Researchers are scanning the skies for them.
-
 Animals
AnimalsConservationists should make friends with hunters
A survey of outdoor enthusiasts in rural New York finds that both hunters and birdwatchers are likely to engage in conservation behaviors, such as donating money.
-
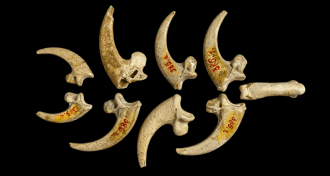 Anthropology
AnthropologyCache of eagle claws points to Neandertal jewelry-making
Eagle-claw jewelry points to Neandertals’ symbolic behavior before contact with humans, researchers argue.
By Bruce Bower -
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceBright patches on Ceres are plumes of water, maybe
Bright patches on Ceres could be plumes of water venting into space.
-
 Animals
AnimalsWhy orangutans cup their mouths to sound an alarm
Orangutans might use their hands to lower the pitch of alarm calls, a study suggests.