Feature
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceYear in review: The nose knows a trillion odors
Humans can suss out more than 1 trillion different smells, a 2014 study estimated.
By Bruce Bower -
 Archaeology
ArchaeologyYear in review: Roster of dinosaurs expands
With the discovery of several new species and a few dogma-shaking revelations, dinosaurs got a total rethink in 2014.
By Meghan Rosen -
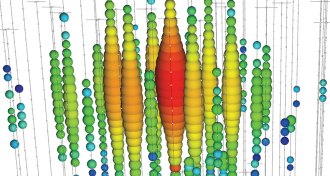 Particle Physics
Particle PhysicsYear in review: Neutrinos leave tracks in ice
The IceCube experiment has started to pinpoint the birthplaces of some high-energy neutrinos.
By Andrew Grant -
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceYear in review: Ocean may power Enceladus’ geysers
NASA’s Cassini spacecraft builds a stronger case for a subsurface ocean on Enceladus that drives ice geysers on the moon’s south pole.
-
 Animals
AnimalsYear in review: The post-pigeon century
Birds' troubles received an eerie emphasis in the news when biologists marked the 100th anniversary of the death of the last known passenger pigeon.
By Susan Milius -
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceYear in review: Business booming on Mars
Mars now has seven robots studying it and together they have given scientists their best view of any planet in the solar system other than Earth.
-
 Humans
HumansYear in review: Genes, bones tell new Clovis stories
The genes and bones of the Clovis people reveal the range and legacy of the early North Americans.
By Bruce Bower -
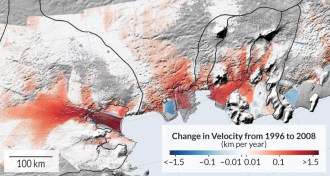 Climate
ClimateYear in review: Climate warnings heat up
Climate change is here and the world is unprepared, scientists and policy makers declared multiple times in 2014.
By Beth Mole -
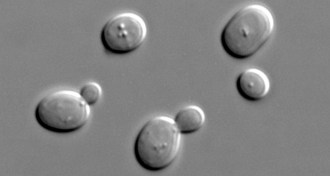 Genetics
GeneticsYear in review: Life’s complexity recoded
New genetic letters in bacteria and a simplified yeast chromosome showcase scientists' advances in understanding the simplicity and complexity of life.
-
 Environment
EnvironmentYear in review: Microbes exploit their killer
Triclosan, an unregulated antimicrobial chemical found in consumer products, may aid, rather than deter, microbes that invade people’s bodies.
By Beth Mole -
 Tech
TechDesigning robots to help in a disaster
Ideally, robots could take over for human crews in disaster zones. But seemingly simple tasks, such as walking, communicating and staying powered up, still pose big challenges.
By Meghan Rosen -
 Earth
EarthStudying a volcano in a war zone
New isotope analyses offer bad news for the people of Goma, a burgeoning city in the Democratic Republic of the Congo: Mount Nyiragongo may be more dangerous than expected.