News in Brief
-
 Astronomy
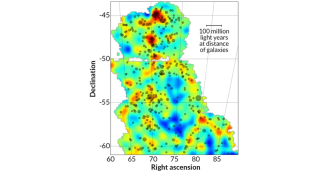
AstronomyMap pinpoints location of invisible dark matter
Dark matter can’t be seen, but a new map shows where it’s hiding. The map confirms that the mysterious matter is concentrated in regions that contain a lot of ordinary matter in the form of galaxy clusters.
By Andrew Grant -
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceComet 67P shows no sign of magnetism
Philae found no evidence of a magnetic field on comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko, but did send back some clues about its rough landing.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyAfterglow alerts astronomers to gamma-ray burst
Astronomers have spotted the remnant glow from a gamma-ray burst without first observing its beam of high-energy gamma rays.
By Andrew Grant -
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceMarijuana component fights epilepsy
A buzz-free extract of marijuana could help epilepsy patients whose seizures resist other treatments.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Paleontology
PaleontologyFossil reveals terror bird’s power
Bones of a new terror bird confirm the creatures used their beaks to hatchet their prey but also raise questions about what drove the birds extinct.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMutation regions mapped on genes that cause breast and ovarian cancer
An analysis of mutated BRCA genes could someday be used for personalized medicine in the fight against breast and ovarian cancer.
By Nathan Seppa -
 Environment
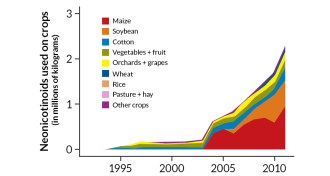
EnvironmentControversial insecticide use rises as farmers douse seeds
Use of neonicotinoids, a class of controversial insecticides, has risen dramatically, posing threat to pollinating insects.
By Beth Mole -
 Climate
ClimateCanadian glaciers face drastic demise
Western Canadian glaciers will shrink 70 percent by 2100, a detailed melting simulation suggests.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyAncient Homo fossils found in Kenya
Finds from three individuals add to skeletal diversity of early members of human genus.
By Bruce Bower -
 Particle Physics
Particle PhysicsExotic particle turns out to be quark molecule
Subatomic particles made of quarks can bind together to form molecules, according to a computer simulation of a long-studied mysterious particle.
By Andrew Grant -
 Anthropology
AnthropologyFootprints offer clues about daily hominid life
Early male members of the human genus spent a lot of time together by the water, as their footprints attest.
By Bruce Bower -
 Animals
AnimalsFossilized seashells’ true colors revealed
To the naked eye, fossilized seashells lack the colorful patterns of their living counterparts. But ultraviolet light can reveal some of their unique hues.