News
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineMaternal deaths in the U.S. keep climbing
New U.S. data show that as maternal deaths rise, a large gap between the maternal mortality rate of Black women compared with white women persists.
-
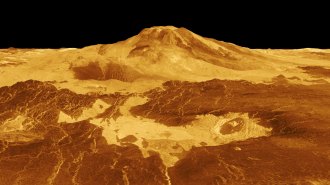 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceA volcano on Venus was spotted erupting in decades-old images
A new look at old data reveals an eruption on Venus in the 1990s that was probably similar to Hawaii’s Kilauea eruption in 2018.
-
 Earth
EarthA moon-forming cataclysm could have also triggered Earth’s plate tectonics
Deeply buried remnants of a hypothetical planet that slammed into Earth 4.5 billion years ago might have set subduction into motion.
By Nikk Ogasa -
 Animals
AnimalsA ‘fire wolf’ fish could expand what we know about one unusual deep-sea ecosystem
Unlike other known methane seeps, Jacó Scar is slightly warmer than the surrounding water and is a home for both cold-loving and heat-loving organisms.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsWhy experts recommend ditching racial labels in genetic studies
Racial labels don’t explain biological and genetic diversity but do cause stigma. They belong “in the dustbin of history,” a panel of experts says.
-
 Tech
TechA trick inspired by Hansel and Gretel could help rovers explore other worlds
Taking a cue from a classic fairy tale, scientists propose a way for rovers to send back data from treacherous terrain.
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceIn mice, anxiety isn’t all in the head. It can start in the heart
Scientists used optogenetics to raise the heartbeat of a mouse, making it anxious. The finding could offer a new angle for studying anxiety disorders.
-
 Life
LifeHoneybees waggle to communicate. But to do it well, they need dance lessons
Young honeybees can’t perfect waggling on their own after all. Without older sisters to practice with, youngsters fail to nail distances.
By Susan Milius -
 Archaeology
ArchaeologySome monkeys accidentally make stone flakes that resemble ancient hominid tools
A study of Thailand macaques raises questions about whether some Stone Age cutting tools were products of planning or chance.
By Bruce Bower -
 Astronomy
AstronomyA runaway black hole has been spotted fleeing a distant galaxy
A bright streak stretching away from a remote galaxy might be the light from stolen gas and new stars caught in the wake of an escaping black hole.
-
 Paleontology
Paleontology520-million-year-old animal fossils might not be animals after all
Newly described fossils of Protomelission gatehousei suggest that the species, once thought to be the oldest example of bryozoans, is actually a type of colony-forming algae.
By Sid Perkins -
 Climate
ClimateHow wildfires deplete the Earth’s ozone layer
Scientists detail the chain of chemical reactions that occur when wildfire smoke enters the stratosphere.