News
-
 Earth
EarthReawakened Yellowstone geyser isn’t a sign of imminent explosion
The 2018 reactivation of Yellowstone’s Steamboat Geyser isn’t a portent of dangerous volcanic or hydrothermal eruptions, scientists say.
-
 Health & Medicine
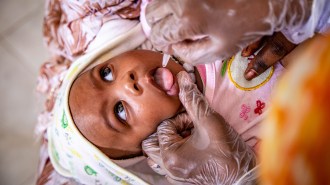
Health & MedicineA new polio vaccine joins the fight to vanquish the paralyzing disease
Work on the ground to vaccinate children continues in the push to finally eradicate polio.
-
 Chemistry
ChemistryThis weird chemical bond acts like a mash-up of hydrogen and covalent bonds
Chemistry students are taught that hydrogen bonds and covalent bonds are distinct, but a new study shows they exist on a continuum.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsSome identical twins don’t have identical DNA
Mutations arising early in development may account for genetic differences between identical twins.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyIce Age hunters’ leftovers may have fueled dog domestication
Ancient people tamed wolves by feeding them surplus game, researchers suggest.
By Bruce Bower -
 Health & Medicine
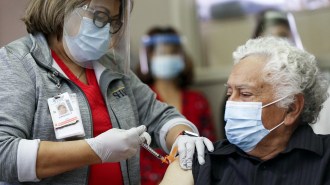
Health & MedicineSevere allergic reactions to COVID-19 vaccines are extremely rare, CDC says
Out of the first 1.9 million doses of Pfizer’s COVID-19 vaccine given in the United States, there were 21 reported cases of anaphylaxis, a CDC study finds.
-
 Genetics
GeneticsPlague may have caused die-offs of ancient Siberians
DNA suggests that the deadly bacterium that causes the plague reached northeast Asia by 4,400 years ago.
By Bruce Bower -
 Chemistry
ChemistryZinc-air batteries are typically single-use. A new design could change that
Swapping out the electrolyte in zinc-air batteries helps these next-gen power sources last longer.
-
 Animals
AnimalsThese spiders may sew leaves into fake shelters to lure frogs to their doom
Madagascar’s huntsman spiders use silk to turn two leaves into a cool hollow. Such microhabitats may appeal to the spiders’ prey, a study suggests.
By Jake Buehler -
 Climate
ClimateWhat the pandemic can teach us about ways to reduce air pollution
Data collected during COVID-19 shutdowns may help tease out the complicated chemistry that brews poor air quality.
-
 Earth
EarthPlastic drinking water pipes exposed to high heat can leak hazardous chemicals
Lab tests exposing commonly used water pipes to wildfire-like heat show damaged pipes can leach the carcinogen benzene and other chemicals.
By Megan Sever -
 Space
SpaceHow future spacecraft might handle tricky landings on Venus or Europa
Scientists are getting inventive with ways to touch down on these worlds, where landers will face obstacles not seen elsewhere in the solar system.