News
-
 Agriculture
AgricultureBirds fed a common pesticide lost weight rapidly and had migration delays
Scientists have previously implicated neonicotinoid pesticides in declining bee populations. Now a study suggests that songbirds are affected, too.
By Maanvi Singh -
 Tech
TechThis device harnesses the cold night sky to generate electricity in the dark
A new thermoelectric generator uses the temperature difference between Earth and outer space to create electricity after the sun goes down.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyThis may be the first known exoplanet with rain and clouds of water droplets
For the first time, astronomers have detected water vapor and possibly signs of clouds and even rain in the air of a potentially habitable exoplanet.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyGiant radio bubbles spew from near the Milky Way’s central black hole
New structures found at the heart of our galaxy join other bubbles, chimneys and filaments that hint at a turbulent past.
-
 Humans
HumansArtists who paint with their feet have ‘toe maps’ in their brains
Brain specialization comes with toe specialization in people who use their feet for painting, eating and writing.
-
 Physics
PhysicsPhysicists may be a step closer to solving the mystery of proton size
Multiple measurements now agree that the proton is smaller than previously thought.
-
 Tech
TechA new prosthetic leg that senses touch reduces phantom pain
A prosthetic leg that can sense foot pressure and knee angle helped two men walk faster and reduced phantom leg pain.
-
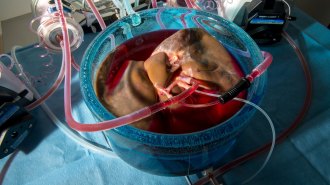 Humans
HumansSupercooling tripled the shelf life of donor livers
Cooling organs to subzero temperatures could help them last longer, making lifesaving transplants available to more people.
-
 Earth
EarthAncient crystal growths in caves reveal seas rose 16 meters in a warmer world
The Pliocene era cave formations on the Spanish coast of Mallorca offer hints about how oceans could respond to human-driven climate change.
-
 Humans
HumansVaping is suspected in a fifth death and hundreds of injuries
U.S. health officials can’t yet point to a substance or device that’s behind a rising number of severe lung injuries and deaths tied to e-cigarettes.
-
 Space
SpaceIndia lost contact with its first lunar lander just before touchdown
Chandrayaan 2 mission officials are trying to figure out why its rover-carrying lander went silent moments before it was to reach the moon’s surface.
-
 Humans
HumansThe longest Dead Sea Scroll sports a salt finish that the others lack
A newly discovered salty lamination on the Temple Scroll could help explain why the ancient manuscript’s parchment is remarkably bright.