News
-
 Life
LifeSpraying bats with ‘good’ bacteria may combat deadly white nose syndrome
Nearly half of bats infected with white nose syndrome survived through winter after being spritzed with antifungal bacteria, a small study finds.
-
 Tech
TechThis solar-powered device produces energy and cleans water at the same time
Someday, the two-for-one machine could help curb electricity and freshwater shortages.
-
 Earth
Earth3 questions seismologists are asking after the California earthquakes
After back-to-back quakes, scientists are scrambling to figure out which faults ruptured and what it means for future California quake activity.
-
 Artificial Intelligence
Artificial IntelligenceArtificial intelligence has now pretty much conquered poker
A new artificial intelligence called Pluribus is a real card shark at six-player no-limit Texas Hold’em.
-
 Planetary Science
Planetary ScienceHayabusa2 may have just snagged bits of asteroid Ryugu’s insides
In its second sampling attempt, Hayabusa2 became the first spacecraft to try to pick up some of an asteroid’s guts.
-
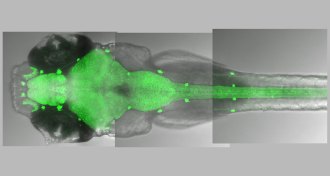 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceBoth fish and humans have REM-like sleep
Sleeping zebrafish have brain and body activity similar to snoozing mammals, suggesting that sleep evolved at least 450 million years ago.
-
 Anthropology
AnthropologyA Greek skull may belong to the oldest human found outside of Africa
Humans possibly reached southeastern Europe by 210,000 years ago.
By Bruce Bower -
 Astronomy
AstronomyMoons that escape their planets could become ‘ploonets’
If giant planets in other star systems lose their moons, the freed objects could become “ploonets,” and current telescopes may be able to find them.
-
 Oceans
OceansA mysterious coral disease is ravaging Caribbean reefs
Scientists are racing to learn what’s behind a disease that’s “annihilating” whole coral species in hopes of stopping it.
-
 Animals
AnimalsGround beetle genitals have the genetic ability to get strange. They don’t
A new look at the genetics of sex organs finds underpinnings of conflicts over genital size.
By Susan Milius -
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineBreaking down the science behind some of your favorite summer activities
Inject some science into your summer.
-
 Oceans
OceansThe largest seaweed bloom ever detected spanned the Atlantic in 2018
Nutrient-rich water from the Amazon River may be helping massive seaweed mats to flourish each summer in the Atlantic Ocean.