News
-
 Climate
ClimateThe Arctic is burning and Greenland is melting, thanks to record heat
A heat wave is melting Greenland’s ice and fueling blazes across the Arctic that are pumping record amounts of carbon dioxide into the air.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineHospitalizations highlight potential dangers of e-cigs to teens’ lungs
E-cigarette use can harm the lungs, and eight Wisconsin teens who developed severe lung injuries after vaping may be the latest victims.
-
 Science & Society
Science & SocietyPublic trust that scientists work for the good of society is growing
More Americans trust the motives of scientists than of journalists or politicians.
By Katy Daigle -
 Astronomy
AstronomyStars may keep spinning fast, long into old age
NASA’s TESS telescope has spotted an old star that spins too fast for theory to explain, suggesting that stars may have a magnetic midlife crisis.
-
 Life
LifeMonkeys can use basic logic to decipher the order of items in a list
Rhesus macaque monkeys don’t need rewards to learn and remember how items are ranked in a list, a mental feat that may prove handy in the wild.
By Bruce Bower -
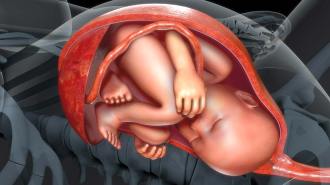 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA new study challenges the idea that the placenta has a microbiome
A large study of more than 500 women finds little evidence of microbes in the placenta, contrary to previous reports on the placental microbiome.
-
 Tech
TechTiny magnetic coils could help break down microplastic pollution
Carbon nanotubes designed to release plastic-eroding chemicals could clear the long-lasting trash from waterways.
-
 Astronomy
AstronomyTESS has found the first-ever ‘ultrahot Neptune’
NASA’s TESS telescope has spotted a world that could be a bridge between other types of exoplanets: hot Jupiters and scorched Earths.
-
 Particle Physics
Particle PhysicsHow a 2017 radioactive plume may be tied to Russia and nixed neutrino research
A botched attempt at producing radioactive material needed for a neutrino experiment may have released ruthenium-106 to the atmosphere in 2017.
-
 Life
LifeImmune system defects seem to contribute to obesity in mice
Subtle defects affecting T cells altered the animals’ microbiome and fat absorption, providing hints of what might also be going on in people.
-
 Particle Physics
Particle PhysicsDark matter particles won’t kill you. If they could, they would have already
The fact that no one has been killed by shots of dark matter suggests the mysterious substance is relatively small and light.
-
 Climate
ClimateHow today’s global warming is unlike the last 2,000 years of climate shifts
Temperatures at the end of the 20th century were hotter almost everywhere on the planet than in the previous two millennia.